Basic Introduction of Return Air Diffusers
At AIREVERPEAK, we take pride in our dedicated craftsmanship in producing HVAC Return Air Diffusers. With a rich heritage of precision engineering, our factory stands at the forefront of HVAC solutions, specifically tailored for efficient air return systems. Our products are the embodiment of innovation, designed to meet the dynamic needs of modern buildings and industrial spaces.
Global Reach, Diverse Offerings
Our global footprint extends to over 150 countries, underlining our commitment to meet diverse customer needs. With a product catalog boasting over 1000 specification varieties across 26 categories, we cater to a broad spectrum of requirements. Notably, many of our products proudly bear the distinction of being recognized as “high-tech products.”
30 Years of Innovation
For nearly 30 years, AIREVERPEAK has been synonymous with quality and innovation in HVAC technology. We’ve dedicated ourselves to perfecting the design and functionality of our Return Air Diffusers, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of modern spaces.
Customized Solutions
We understand that each space is unique, and our approach to HVAC solutions reflects this belief. Our team works closely with clients to create customized diffusers that fit their specific requirements, offering a blend of efficiency, aesthetics, and durability.
Our Expertise:
- Experience and Reliability: With three decades in the business, our experience speaks for itself. We’ve built a reputation for reliability and excellence.
- Innovative Design: We continually invest in research and development, ensuring our products are at the cutting edge of HVAC technology.
- Unmatched Quality: Our manufacturing process adheres to the highest standards, resulting in products that are not only efficient but also durable and reliable.
- Personalized Customer Service: Every client is unique, and so is our service. We pride ourselves on our responsive and personalized customer support.
Basic styles and sizes of Return Air Diffusers
HVAC Return Air Diffusers
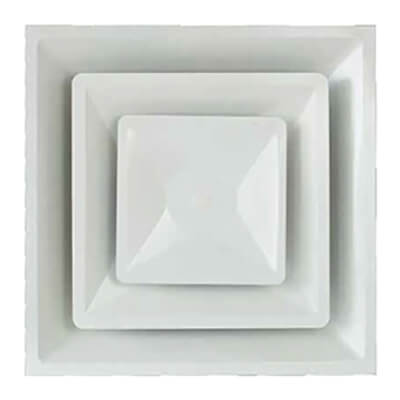 |  |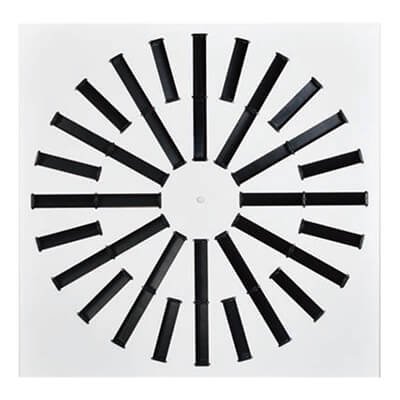  |
| Square Air Diffusers | Exhaust Air Louvre | Swirl Air Diffusers |
 |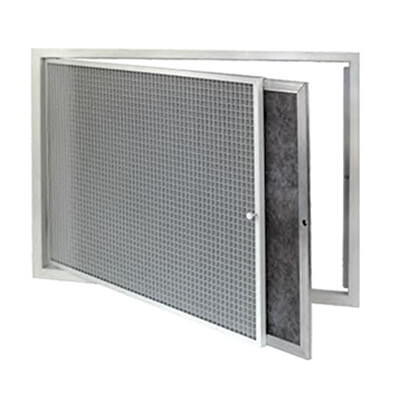  |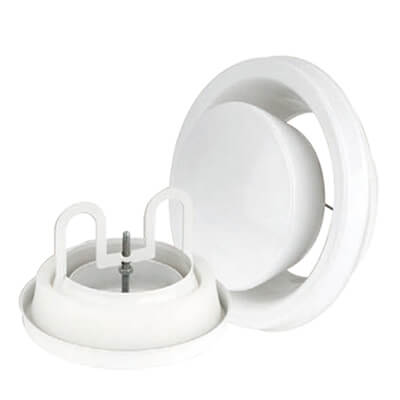  |
| Weatherproof Louvre | Eggcrate Air Diffusers | Exhaust Air Disc Valves |
 |  |  |
| Plastic Air Diffusers | Floor Air Diffusers | Linear Slot Diffusers |
HVAC Air Diffusers – American & Australian
 |  |
| Air Diffusers-American series | Air Diffusers-Australian series |
Catalog of HVAC Air Diffusers:
- Catalog of HVAC Air Valves
- Catalog of HVAC Swirl Diffusers
- Catalog of HVAC Jet Diffusers
- Catalog of HVAC Round Air Ceiling Diffusers
- Catalog of HVAC Square Air Ceiling Diffusers
- Catalog of HVAC Linear Slot Diffuser
- Catalog of HVAC Egg Crate Diffusers
- Catalog of HVAC Plastic Diffusers
- Catalogue of HVAC Exhaust Air Louvre

If you want to know more, please click below:
- HVAC Linear Slot Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Egg Crate Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Jet Nozzle Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Linear Bar Grilles – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Air Swirl Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Return Air Grille – The Ultimate Guide
- Exhaust Air Louver – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Registers – The Ultimate Guide
HVAC Return Air Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
1. What is a Return Air Diffuser?
A return air diffuser is a component in an HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system. Its main function is to collect used air from a room and return it to the HVAC system for reconditioning. This process helps maintain a balanced air circulation, contributing to the overall efficiency of the HVAC system and ensuring a comfortable indoor environment. Typically found on walls or ceilings, return air diffusers are essential for effective air management in residential and commercial buildings.
2. What is the Function of a Return Air Diffuser?
The function of a Return Air Diffuser is integral to the effective and efficient operation of HVAC systems. Its role in air recirculation, maintaining pressure balance, improving air quality, aiding in temperature regulation, enhancing energy efficiency, and contributing to humidity control underscores its importance in HVAC design. Optimally functioning return air diffusers are key to ensuring a comfortable, healthy, and energy-efficient indoor environment.
Main Function of a Return Air Diffuser
- Air Recirculation: The diffuser collects air from within a room or building and directs it back to the HVAC system. This is essential for the continuous cycle of air conditioning, heating, or ventilation.
- Maintaining Air Pressure Balance: By efficiently returning air to the system, return air diffusers help maintain a balanced air pressure within the space. This balance is crucial to prevent strain on the HVAC system and ensure effective operation.
- Improving Indoor Air Quality: As air is returned to the HVAC system, it often passes through filters. The return air diffuser aids in this process, ensuring that the air being recirculated is filtered and free of contaminants like dust, allergens, and pollutants.
Additional Aspects of Functionality
- Temperature Regulation: In systems with heating or cooling capabilities, the return air diffuser contributes to the regulation of room temperature by continuously cycling air through the system, where it’s reconditioned before being redistributed.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper functioning of return air diffusers can enhance the energy efficiency of an HVAC system. Efficient recirculation of air reduces the workload on the system, thereby conserving energy.
- Humidity Control: In conjunction with the HVAC system, return air diffusers can play a role in managing the humidity levels of a room, contributing to a more comfortable environment.
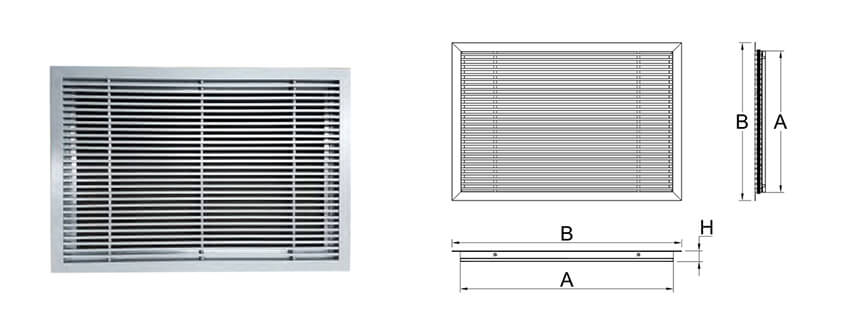
3. How does the Return Air Diffuser compare with the Register?
Comparing a Return Air Diffuser with a Register in an HVAC system highlights several key differences, primarily in terms of function, design, and application. Return Air Diffusers and Registers serve distinct roles in an HVAC system – the former focusing on returning air to the system for reconditioning, and the latter on delivering conditioned air into the space. While a return air diffuser is more about functionality and efficiency in air circulation, a register combines functionality with user control over airflow and aesthetic considerations.
Function and Purpose
- Return Air Diffuser:
- Its main function is to facilitate the return of air from the room back to the HVAC system for reconditioning (heating/cooling) and filtration.
- It plays a vital role in maintaining air circulation and pressure balance within the HVAC system.
- Register:
- A register is typically used for the supply side of the HVAC system. It delivers conditioned air (heated or cooled) from the HVAC system into the room.
- Registers often have adjustable dampers or louvers, allowing control over the direction and volume of airflow into the space.
Design Features
- Return Air Diffuser:
- Generally, features a more simplistic design without adjustable parts. It often has larger openings to accommodate the volume of returning air.
- The focus is on maximizing airflow back to the HVAC system with minimal resistance.
- Register:
- Includes adjustable components, like louvers or dampers, to direct and regulate airflow.
- Often designed to disperse air in specific patterns for efficient heating or cooling of a space.
Placement and Aesthetics
- Return Air Diffuser:
- Typically placed in strategic locations to efficiently capture air from the room. Can be located on walls, ceilings, or floors.
- Aesthetic design may be less varied, as the primary focus is on functionality.
- Register:
- Found in areas where conditioned air needs to be distributed effectively. Placement is often under windows, near the floor, or on the ceiling.
- Comes in a variety of styles and finishes to match room decor, as they are more visible and integral to room aesthetics.
4. What are the Common Types of Return Air Diffusers?
Return air diffusers are an essential component in HVAC systems, designed to facilitate the efficient return of air to the system for reconditioning. These diffusers come in various types, each suited to different architectural requirements and airflow needs. Here’s a rundown of the common types:
1. Standard Return Air Diffusers
- Design: Typically features a simple, unobtrusive design with a grille or louvers.
- Application: Common in residential and commercial buildings for general return air purposes.
2. Filter Return Grilles
- Design: Equipped with a filter, these diffusers not only facilitate air return but also help in filtering out dust and other airborne particles.
- Application: Ideal for environments where maintaining air purity is a priority, such as in homes, offices, or healthcare facilities.
3. Ceiling Return Air Diffusers
- Design: Designed to be installed in the ceiling, these diffusers can have a grille or perforated face for efficient air capture.
- Application: Commonly used in office buildings, retail spaces, and residential settings where ceiling installation is preferred for aesthetic or functional reasons.
4. Wall-Mounted Return Air Diffusers
- Design: These are installed on walls and can range from basic grille designs to more decorative options.
- Application: Suitable for rooms where ceiling installation is not feasible or where specific architectural aesthetics are desired.
5. Floor Return Air Diffusers
- Design: Specifically designed for floor installation, often with robust construction to withstand foot traffic.
- Application: Used in buildings with raised floors or in spaces where wall or ceiling installation is not suitable.
6. Linear and Slot Return Diffusers
- Design: Feature a linear or slot design, offering a more modern and discreet appearance.
- Application: Ideal for contemporary spaces or in areas where a more subtle air return solution is desired.
7. Plenum Return Air Diffusers
- Design: These diffusers are designed to connect directly to the plenum box, efficiently channeling return air back to the HVAC system.
- Application: Used in specialized HVAC setups, particularly in commercial and industrial environments.
The choice of a return air diffuser depends on factors such as the architectural design of the space, airflow requirements, and aesthetic preferences. From standard and filter return grilles to more specialized options like linear and plenum diffusers, each type offers unique features for efficient air return in different environments. Selecting the appropriate type of return air diffuser ensures optimal performance of the HVAC system, contributing to effective air circulation and a comfortable indoor climate.

5. What Parameters Determine the Sizing of the Supply & Return Air Diffuser?
Let’s check out a video for review:
The sizing of supply & return air diffusers is determined by a combination of room size and volume, airflow requirements, duct size, room occupancy, and usage, as well as comfort and noise considerations. Accurate calculation of these parameters ensures that the selected diffuser efficiently distributes air throughout the space, maintaining comfort and optimizing the performance of the HVAC system.
1. Room Size and Volume
- Calculation of Room Volume: The size and volume of the room (length, width, and height) are fundamental in determining the amount of air that needs to be circulated.
- Air Changes Per Hour (ACH): Different types of spaces require different rates of air changes per hour for optimal comfort and air quality. For instance, living spaces may have different ACH requirements compared to storage areas.
2. Airflow Requirements
- Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM): The required airflow rate, measured in cubic feet per minute, is a crucial parameter. It’s calculated based on the room’s volume and the desired ACH.
- HVAC System Capacity: The capacity of the existing HVAC system also influences the diffuser size, as it must be able to deliver the calculated CFM efficiently.
3. Duct Size and System Design
- Ductwork Compatibility: The size and layout of the existing ductwork impact the diffuser sizing. The diffuser must be compatible with the duct size to ensure proper airflow.
- Pressure Loss Considerations: The diffuser should be sized to minimize pressure loss in the system, ensuring efficient operation.
4. Occupancy and Usage of the Space
- Occupancy Level: Higher occupancy levels typically require more air changes for adequate ventilation.
- Room Function: The use of the space influences the required airflow. For example, kitchens or labs might need more ventilation compared to a standard office.
5. Comfort and Noise Considerations
- Air Distribution for Comfort: The diffuser should be sized to provide even air distribution without creating drafts or hot/cold spots.
- Noise Level: Larger diffusers can often handle the required airflow at lower velocities, reducing noise levels for a more comfortable environment.
6. How do Return Air Diffusers and Nozzles compare in an HVAC System?
Return Air Diffusers and Nozzles serve distinct roles in an HVAC system – with diffusers focusing on the efficient return of air to the system, and nozzles providing targeted and high-velocity air supply. The choice between them depends on the specific requirements of the HVAC system, the architectural design of the space, and the desired airflow characteristics.
Return Air Diffusers
- Primary Function: Return air diffusers are designed to facilitate the return of air from space back to the HVAC system for reconditioning and filtration.
- Design and Placement: Typically, they have a larger surface area with fewer restrictions to airflow, allowing for the efficient capture and return of a larger volume of air. They are usually placed in strategic locations to maximize air recirculation.
- Airflow Characteristics: The focus of return air diffusers is on gentle, unobstructed air collection rather than direct air distribution, which helps maintain consistent air pressure and quality in the HVAC system.
Air Nozzles
- Primary Function: Nozzles in an HVAC system are used for the targeted delivery of air. They are particularly effective in directing air to specific areas or creating specific airflow patterns.
- Design and Placement: Nozzles are smaller and more directional compared to diffusers. They can be adjusted to direct airflow precisely, making them suitable for spaces that require targeted ventilation or where air needs to be distributed over a long distance.
- Airflow Characteristics: Air nozzles can deliver air at higher velocities and are often used in applications where rapid air mixing or specific directional control is needed.
Key Differences
- Purpose in HVAC System: Return air diffusers are primarily for air return, aiding in air quality and circulation, whereas nozzles are for precise air supply, focusing on specific airflow requirements.
- Design Considerations: Diffusers are generally designed to blend into the architectural aesthetics of a space and provide quiet operation, whereas nozzles may be more functional in appearance and capable of handling high-velocity airflow.
- Application: Return air diffusers are a standard requirement in most HVAC systems for efficient operation, while nozzles are used for specialized applications, such as in large open spaces, industrial environments, or areas requiring focused air distribution.

7. What are the Benefits of a Return Air Diffuser?
The benefits of a Return Air Diffuser in an HVAC system are substantial, encompassing efficient air circulation, improved indoor air quality, energy efficiency, enhanced comfort, and versatility in design and application. These advantages underscore the importance of return air diffusers in achieving a functional, comfortable, and cost-effective indoor climate.
1. Efficient Air Circulation
- Enhanced Airflow: Return air diffusers facilitate the efficient return of air from a room back to the HVAC system. This continuous circulation of air is essential for maintaining consistent temperature and air quality.
- Balanced HVAC System: By ensuring efficient air return, these diffusers help maintain a balanced and efficient HVAC system, preventing issues like pressure imbalances or air stagnation.
2. Improved Indoor Air Quality
- Air Filtration: As air is returned to the HVAC system, it often passes through filters. Return air diffusers aid in this process, helping to remove contaminants such as dust, allergens, and pollutants from the air.
- Reduction of Humidity and Odors: Effective air circulation helps in managing humidity levels and reducing odors, contributing to a more comfortable and healthier indoor environment.
3. Energy Efficiency
- Reduced Energy Consumption: By aiding in the efficient operation of the HVAC system, return air diffusers can help reduce energy consumption. Efficient air circulation means the system doesn’t have to work as hard to heat or cool the space.
- Cost Savings: Lower energy consumption translates to cost savings on energy bills, making return air diffusers a financially beneficial component in the long run.
4. Enhancing Comfort
- Even Temperature Distribution: Proper air circulation facilitated by return air diffusers helps in maintaining even temperature distribution within a space, eliminating hot or cold spots.
- Adjustable Comfort Levels: In systems where diffusers are adjustable, they can be optimized for specific comfort levels based on occupancy and use of space.
5. Versatility in Design and Application
- Aesthetic Integration: Return air diffusers come in various designs and can be selected to complement the aesthetic of the space.
- Suitability for Various Spaces: They can be installed in a range of environments, from residential to commercial spaces, offering flexibility in HVAC system design.
8. Can you get a Replacement for the Return Air Diffuser?
Yes, you can get a replacement for a Return Air Diffuser in your HVAC system. Over time, diffusers may wear out, or become damaged, or you might simply want to upgrade to a newer model for efficiency, better air quality, or aesthetic reasons.
Steps for Replacing a Return Air Diffuser
- Identify the Need for Replacement:
- Assess whether the diffuser is damaged, functioning inefficiently, or no longer fits the aesthetic of the space.
- Consider replacing if it’s contributing to poor air circulation, noise, or energy inefficiency.
- Determine the Correct Size and Type:
- Measure the existing diffuser and the opening it occupies to ensure you purchase the correct size.
- Decide on the type of diffuser based on the specific needs of your space, such as airflow requirements, noise level, and design preferences.
- Selecting a New Diffuser:
- Choose a new diffuser that meets your HVAC system’s requirements and complements the interior design of your space.
- Consider energy-efficient models or those with enhanced filtration features for improved performance.
- Purchasing from a Reputable Supplier:
- Buy from a reputable HVAC supplier or manufacturer to ensure quality and compatibility.
- Check warranty and support options for the new diffuser.
- Installation:
- If you are experienced with HVAC systems, you may be able to perform the replacement yourself. Ensure the HVAC system is turned off before starting the work.
- For more complex systems or to ensure proper installation, hiring a professional HVAC technician is recommended.
Considerations for Replacement
- Compatibility with HVAC System: The new diffuser must be compatible with your existing HVAC system in terms of size, airflow capacity, and design.
- Aesthetic Integration: If interior aesthetics are important, consider the design and look of the new diffuser to ensure it fits well with your space.
- Budget and Cost-Effectiveness: Balance the cost of the new diffuser with the benefits it offers, including potential energy savings and improved air quality.
Replacing a Return Air Diffuser can be a straightforward process, provided you accurately identify the need, select the appropriate size and type, and purchase from a reliable source. A new diffuser can significantly enhance air circulation, energy efficiency, and the overall comfort of your indoor environment.

9. What Factors do you Consider when Looking for Ideal Material for a Return Air Diffuser?
Selecting the ideal material for a Return Air Diffuser is a crucial decision that impacts the efficiency, durability, and overall performance of your HVAC system. The right material can also influence the aesthetic appeal of the diffuser within the space.
1. Environmental Conditions
- Moisture and Corrosion Resistance: In humid or coastal areas, materials that resist moisture and corrosion, such as aluminum or stainless steel, are preferable.
- Temperature Tolerance: The material should withstand the typical temperature ranges of the environment without warping or degrading.
2. Durability and Longevity
- Strength and Wear Resistance: Choose materials known for their strength and ability to withstand wear and tear over time, ensuring longevity.
- Maintenance Requirements: Consider how easy the material is to clean and maintain, as some materials may require more frequent maintenance than others.
3. Aesthetic Considerations
- Design and Finish: The material should align with the interior design of the space. Many materials come with different finishes and styles to match various décor themes.
- Color Retention: Materials that maintain their color and finish over time, without fading or discoloration, are ideal for maintaining aesthetics.
4. Air Quality and Safety
- Non-Toxicity: Ensure the material does not emit harmful substances or degrade air quality, especially in enclosed spaces.
- Fire Resistance: In some environments, fire-resistant materials might be required for safety compliance.
5. Efficiency of Air Distribution
- Airflow Characteristics: The material should complement the design of the diffuser to ensure efficient air distribution and performance of the HVAC system.
6. Cost-Effectiveness
- Initial Cost vs. Long-Term Value: While some materials may be more costly upfront, their durability and lower maintenance needs can offer better long-term value.
- Energy Efficiency: Some materials may contribute to better energy efficiency of the system, which can lead to cost savings.
7. Compliance with Regulations
- Building Codes and Standards: The chosen material should comply with local building codes and HVAC industry standards.
When selecting the ideal material for a Return Air Diffuser, it’s important to consider environmental conditions, durability, aesthetic preferences, air quality, safety, efficiency in air distribution, cost-effectiveness, and regulatory compliance. Balancing these factors will help in choosing a material that not only ensures the efficient operation of the HVAC system but also fits well with the design and functional requirements of the space.
10. What is the difference between a Return Air Diffuser and Exhaust Air Diffuser?
The difference between a Return Air Diffuser and an Exhaust Air Diffuser lies primarily in their function and application within an HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system. While both types of diffusers play crucial roles in air management, they serve distinct purposes. Return air diffusers focus on recirculating indoor air back to the system, and exhaust air diffusers are responsible for expelling unwanted indoor air to the outside.
Return Air Diffuser
- Function:
- Return Air Diffusers are designed to facilitate the movement of air from indoor spaces back to the HVAC system. This air is then reconditioned – heated or cooled – and filtered before being recirculated.
- Design:
- Typically feature larger openings or grilles to efficiently handle the volume of return air. They are designed to minimize resistance to airflow to ensure an efficient return to the system.
- Placement:
- Often strategically located in rooms or hallways to capture the maximum amount of indoor air and maintain effective circulation.
- Air Quality Contribution:
- By returning air to the HVAC system for filtration, they contribute significantly to maintaining indoor air quality.
Exhaust Air Diffuser
- Function:
- Exhaust Air Diffusers are used to expel air from inside a building to the outside. They are key in removing stale, contaminated, or humid air from indoor environments.
- Design:
- Designed to direct air outwards, often connected to ducts leading to the exterior of the building. They may have features to prevent backdrafts and ensure a one-way flow of air.
- Placement:
- Commonly found in bathrooms, kitchens, or industrial settings where there is a need to regularly expel odorous or contaminated air.
- Air Quality Contribution:
- While they don’t recirculate air, they play a crucial role in removing undesirable air from indoor spaces, thus contributing to overall air quality by preventing stagnation.
Key Differences
- Direction of Air Flow: Return air diffusers circulate air back into the HVAC system for reconditioning, whereas exhaust air diffusers expel air out of the building.
- Contribution to HVAC System: Return diffusers are integral to the recirculation process in HVAC systems, while exhaust diffusers are critical for removing air that should not be recirculated.
- Usage Areas: Return air diffusers are used across various indoor spaces for general air circulation, whereas exhaust diffusers are specifically used in areas that generate moisture, odors, or pollutants.

11. Where is the Suitable Place to Install the Return Air Diffuser?
The suitable placement of a Return Air Diffuser depends on factors such as the room’s layout, the location of supply vents, the primary use of the space (heating or cooling), and the specific requirements of the building. Central locations, strategic placement away from supply vents, and consideration of room-specific needs are key to ensuring effective air circulation and maintaining a comfortable and healthy indoor environment.
General Guidelines for Placement
- Central Locations: Install return air diffusers in central areas within the space to facilitate even air circulation. Central placement helps in drawing air uniformly from all parts of the room.
- Consider Room Layout: The layout of the room, including the placement of furniture, doors, and windows, should be considered to avoid obstructions to airflow.
- Avoid Conflict with Supply Vents: Place return diffusers away from supply vents or registers to prevent short-circuiting, where the conditioned air is immediately drawn back into the return vent before circulating the room.
Specific Placement Recommendations
- Residential Settings:
- In homes, return diffusers are often placed in hallways or common areas to effectively circulate air from various rooms.
- In individual rooms, placing them on walls opposite to supply vents can promote thorough air mixing.
- Commercial Buildings:
- In larger spaces like offices or retail areas, multiple return diffusers may be required. They should be strategically placed to handle the air volume effectively.
- Installing them in suspended ceiling spaces is common, as it allows for unobtrusive and efficient air return.
- Special Considerations for Specific Rooms:
- In spaces like kitchens or bathrooms, where moisture and odors are prevalent, return diffusers should be positioned to efficiently capture and remove this air.
Height Considerations
- Higher Placement for Heating: In settings primarily used for heating, installing return diffusers at a higher level can be more effective, as warm air rises.
- Lower Placement for Cooling: In environments where cooling is the main function, lower placement may be more efficient, as cool air tends to settle at lower levels.
12. What is the Suitable CFM in a Return Air Diffuser?
Determining the suitable Cubic Feet per Minute (CFM) for a Return Air Diffuser in an HVAC system is crucial for maintaining effective air circulation and ensuring the overall efficiency of the system. The CFM rating indicates the volume of air the diffuser can handle and varies based on room size, usage, and specific HVAC system requirements.
Understanding CFM in HVAC Systems
- CFM Meaning: CFM, or Cubic Feet per Minute, measures the volume of air moved by the HVAC system. In the context of a return air diffuser, it refers to the amount of air it can effectively channel back to the HVAC system.
- Importance of Correct CFM: Proper CFM ensures that the HVAC system can efficiently circulate air, maintain balanced air pressure, and provide consistent temperature and air quality.
Factors Influencing Suitable CFM
- Room Size and Volume: The larger the room, the higher the CFM required. Calculate the room’s volume (length x width x height) to get an initial estimate of needed airflow.
- Air Changes Per Hour (ACH): ACH is the number of times the air in a space should be completely replaced in an hour. Different types of rooms (like living areas, kitchens, or commercial spaces) require different ACH rates.
- HVAC System Capacity: The overall capacity of the HVAC system also determines the suitable CFM for return air diffusers. The system’s capacity should match the combined CFM requirements of all diffusers.
Calculating Suitable CFM
- Basic Formula: The basic formula to estimate CFM for a room is: CFM=(RoomVolumeincubicfeet)×(ACH)/60
- Professional Assessment: For an accurate determination, especially in complex or large spaces, consulting with an HVAC professional is advisable. They can consider additional factors like occupancy, room usage, and system design.
Considerations for Specific Environments
- High Occupancy Areas: Spaces with high occupancy might require a higher CFM for adequate ventilation.
- Rooms with Special Requirements: Areas like kitchens or laboratories, where air quality needs are stringent, may need higher CFM ratings for effective air management.
The suitable CFM for a Return Air Diffuser varies based on the room’s size, the desired air changes per hour, and the capacity of the overall HVAC system. Accurately calculating the required CFM is essential for ensuring that the HVAC system operates efficiently, maintaining comfortable indoor air quality and temperature levels.

13. Is there a difference between a Return Air Diffuser and a Grille?
Yes, there is a difference between a Return Air Diffuser and a Grille in an HVAC system. While return air diffusers and grilles are both integral components of an HVAC system, they serve different purposes with distinct design features. Return air diffusers are specialized for effective air recirculation back to the HVAC system, whereas grilles are more about covering duct openings and may not significantly alter airflow.
Return Air Diffuser
- Primary Function: A Return Air Diffuser is designed to facilitate the efficient return of air from a room or space back to the HVAC system for reconditioning (heating or cooling) and filtration.
- Design Characteristics: Typically, return air diffusers have a larger surface area with minimal obstructions to maximize the volume of air they can return to the system. They are designed for efficient air collection rather than direct air distribution.
- Airflow Dynamics: The focus of return air diffusers is on gentle, unobtrusive air movement, helping maintain consistent air pressure in the HVAC system.
Grille
- Primary Function: A Grille in an HVAC system is often used as a covering over duct openings, both for air supply and return. Its main function is to conceal ductwork and distribute or return air without significantly altering its direction or flow.
- Design Characteristics: Grilles can be simpler in design compared to diffusers and may not always have features like adjustable louvers or dampers. They are more about aesthetics and basic functionality.
- Airflow Dynamics: Grilles are more passive in terms of air management. They do not actively control or direct airflow but rather serve as a barrier or a cover over openings in ductwork.
Key Differences
- Function and Air Management: Return air diffusers are specifically designed for efficient air return with minimal resistance, whereas grilles are more about covering duct openings and may be used for both air supply and return without actively managing airflow.
- Design and Aesthetics: Return air diffusers generally have a more functional design focused on airflow efficiency, while grilles can range from basic to highly decorative, depending on their intended use and location.
- Application: The choice between a return air diffuser and a grille depends on the specific requirements of the HVAC system – whether there is a need for efficient air recirculation or simply a covering for ductwork.
14. How do you Choose a Return Air Diffuser?
Selecting the right Return Air Diffuser involves considering the room size and airflow requirements, the type of HVAC system, diffuser design and features, material, aesthetic preferences, energy efficiency, and noise level. Additionally, the reputation of the manufacturer and product reviews can guide you in making an informed choice.
1. Assess Room Size and Airflow Needs
- Calculate Room Volume: Determine the size of the room where the diffuser will be installed. This involves measuring the length, width, and height of the space.
- Determine Airflow Requirements: Based on the room size, calculate the required airflow rate in cubic feet per minute (CFM). This will help in selecting a diffuser that can handle the necessary air volume.
2. Consider the Type of HVAC System
- System Compatibility: Ensure the diffuser is compatible with your existing HVAC system in terms of size, capacity, and airflow dynamics.
- Type of Use: Whether the system is predominantly used for heating, cooling, or both, will influence the type of diffuser needed.
3. Examine Diffuser Designs and Features
- Design Efficiency: Look for designs that effectively circulate air back to the HVAC system. This might include features like large surface areas or specific grille patterns.
- Adjustable Options: Some diffusers come with adjustable features, allowing you to control the airflow direction and volume.
4. Material and Durability
- Material Choice: Consider the material of the diffuser, which should be durable and suitable for the environment where it will be used. Options include metal (like aluminum or steel), plastic, or even wood.
- Maintenance and Longevity: Select a material that is easy to maintain and clean, and offers longevity under the specific conditions of use.
5. Aesthetic Considerations
- Match with Interior Decor: The diffuser should complement the interior design of the space. Many diffusers come in various styles and finishes to match different decor styles.
- Visibility and Placement: Consider how visible the diffuser will be and select a design that fits well with the aesthetic of the room.
6. Check Energy Efficiency and Noise Level
- Energy Efficiency: A well-designed diffuser can contribute to the overall energy efficiency of the HVAC system.
- Noise Reduction: Consider the noise level of the diffuser, especially in quiet environments like bedrooms or offices.
7. Review Manufacturer Reputation and Product Reviews
- Manufacturer Reliability: Research the reputation of the manufacturer for quality and reliability.
- Read Reviews: Look at customer reviews and feedback on different models and brands.

15. Is there a Shape Limitation for Return Air Diffuser Designs?
No, the design of Return Air Diffusers in HVAC systems, particularly regarding their shape, offers a degree of flexibility to accommodate various architectural and functional needs. While there are some standard shapes commonly used, advancements in manufacturing and design have broadened the possibilities.
Standard Shapes in Return Air Diffusers
- Rectangular and Square Designs: These are the most common shapes for return air diffusers. They are often chosen for their ease of installation and compatibility with a wide range of architectural styles.
- Circular and Round Designs: Round diffusers are also popular, especially in settings where they can complement the aesthetics or where a more even air distribution is desired.
Advancements and Customization
- Custom Shapes: Modern manufacturing techniques have made it possible to create return air diffusers in custom shapes. This allows for greater flexibility in design and the ability to tailor diffusers to specific architectural requirements.
- Architectural Integration: Custom-shaped diffusers can be designed to blend seamlessly with unique architectural features, such as curved walls or intricate ceiling designs.
Functional Considerations
- Efficiency: Regardless of the shape, the primary function of efficiently returning air to the HVAC system must be maintained. The design should ensure minimal resistance to airflow.
- Size and Placement: The effectiveness of a diffuser can also depend on its size and placement, which need to be considered along with shape to ensure optimal functionality.
Aesthetic and Practical Aspects
- Interior Design Compatibility: The shape can be selected based on interior design considerations. Custom shapes offer opportunities to make the diffuser a feature element or to have it discreetly blend into the background.
- Space Limitations: In some cases, the shape may be influenced by space limitations or the layout of the room.
While there are standard shapes for return air diffusers, there is no strict limitation on the shape of these components. Advances in design and manufacturing have expanded the possibilities, allowing for custom shapes that can fit unique architectural needs and aesthetic preferences. However, it is crucial that the chosen shape does not compromise the diffuser’s functional efficiency in air circulation. The shape, along with size and placement, should be considered in the context of the room’s layout and the HVAC system’s requirements to ensure optimal performance.
16. What is the cost of a Return Air Diffuser?
The cost of a Return Air Diffuser can vary widely based on several factors including material, size, design, brand, and any additional features it might have. It’s important to consider both the initial purchase price and the potential long-term benefits such as energy efficiency and durability.
Factors Influencing the Cost
- Material: The choice of material (e.g., aluminum, steel, plastic) plays a significant role in the price. Metal diffusers are generally more expensive than plastic ones, but they often offer greater durability.
- Size and Complexity: Larger and more complex diffusers will typically cost more. The size needed will depend on the room’s size and the HVAC system’s requirements.
- Design and Aesthetic Features: Custom designs or diffusers with aesthetic enhancements (like decorative finishes) can increase the price.
- Brand and Quality: Products from well-known and reputable brands might come at a premium, often due to higher quality standards and better warranty terms.
- Energy Efficiency and Additional Features: Diffusers with features that enhance energy efficiency or provide additional functionalities (like noise reduction or adjustable airflow) can also be more costly.
Average Cost Range
- Basic Models: Simple, basic return air diffusers made from materials like plastic can start from as low as $10 to $30.
- Mid-Range Models: More durable materials, larger sizes, or added features can bring the cost into the range of $30 to $100.
- High-End Models: Premium diffusers, often with custom designs or specialized features, can cost upwards of $100, sometimes reaching several hundred dollars for very high-end or large custom models.
Additional Cost Considerations
- Installation Costs: Depending on whether you can install the diffuser yourself or need professional help, installation costs can add to the total expense.
- Shipping or Handling Fees: If ordering from a distance, shipping or handling fees might also affect the final cost.
The cost of a Return Air Diffuser is influenced by factors like material, size, design, brand, and additional features. Prices can range from relatively inexpensive for basic models to significantly higher for custom or high-end options. When selecting a diffuser, it’s important to balance initial costs with considerations for long-term value, such as durability, efficiency, and the benefits of any additional features.

17. What is the Suitable Color for a Return Air Diffuser?
In most settings, especially residential and commercial buildings, neutral colors (white, off-white, beige, or gray) are preferred for their versatility and ability to integrate seamlessly with various interior designs.
Neutral and Standard Colors
- White: The most common color for return air diffusers is white. It’s a standard choice because of its neutrality and ability to blend with most ceiling and wall colors. White diffusers provide a clean, unobtrusive look that is preferred in many interiors.
- Off-White or Beige: These colors are also popular, especially in spaces where pure white doesn’t match the decor. Off-white or beige can still provide subtlety while complementing warmer color schemes.
- Gray: Light to medium grays are another standard option, offering a modern and slightly more industrial look while still remaining neutral and versatile.
Considerations for Color Selection
- Interior Design Match: The main consideration is how well the color of the diffuser matches the rest of the interior, particularly the ceiling or wall where it will be installed.
- Aesthetic Appeal: While functionality is the primary concern, the visual impact of the diffuser shouldn’t be ignored. It should contribute positively to the overall aesthetic of the space.
- Maintenance and Cleaning: Lighter colors like white may show dust more visibly and might require more frequent cleaning, which is a practical aspect to consider.
Customization and Variations
- Custom Colors: In certain cases, return air diffusers can be painted or customized to match specific color requirements, especially in unique interior designs or branding applications for commercial spaces.
- Metallic Finishes: For metal diffusers, natural metallic finishes (like aluminum or stainless steel) can also be a suitable and aesthetically pleasing option.
18. How do you Size Return Air Diffuser Duct?
Properly sizing the duct for a Return Air Diffuser involves calculating the required airflow based on room volume and usage, matching the duct size to the HVAC system capacity, considering air velocity, and using duct sizing formulas or charts. It’s important to take into account the entire ductwork layout and static pressure to ensure efficient system performance.
1. Determine Room Airflow Requirements
- Calculate Room Volume: Measure the length, width, and height of the space to determine its total volume.
- Air Changes Per Hour (ACH): Decide on the number of air changes per hour needed for the space, which varies depending on room usage (e.g., living spaces, offices, or industrial areas).
- Required Airflow: Calculate the required airflow in cubic feet per minute (CFM) using the formula: CFM=(RoomVolumeincubicfeet)×(ACH)/60
2. Consider HVAC System Capacity
- System Compatibility: Ensure the duct size matches the capacity of the existing HVAC system to handle the calculated CFM without overstraining.
3. Factor in Duct Velocity
- Air Velocity: Consider the recommended air velocity in ductwork. For residential systems, velocities typically range between 700 to 900 feet per minute (FPM), while commercial systems might have higher velocities.
4. Use Duct Sizing Formulas or Charts
- Duct Sizing Equation: Utilize the duct sizing formula or tools like a ductulator. The basic formula relates air velocity, air volume (CFM), and duct cross-sectional area: CFM=Area(insquarefeet)×Velocity(infeetperminute)
- Duct Sizing Chart: Alternatively, use a duct sizing chart, which simplifies the process by correlating duct size with CFM and velocity.
5. Adjust for System Layout
- Ductwork Layout: Consider the layout of the ductwork system, including length, bends, and fittings, which can affect airflow and pressure drop.
6. Account for Static Pressure
- Static Pressure: Ensure that the duct size can handle the static pressure of the system without causing excessive noise or reducing system efficiency.
7. Professional Consultation
- Expert Advice: For accurate sizing, especially in complex systems or large spaces, consulting with an HVAC professional is advisable. They can account for additional factors like local climate, insulation, and specific heating/cooling requirements.
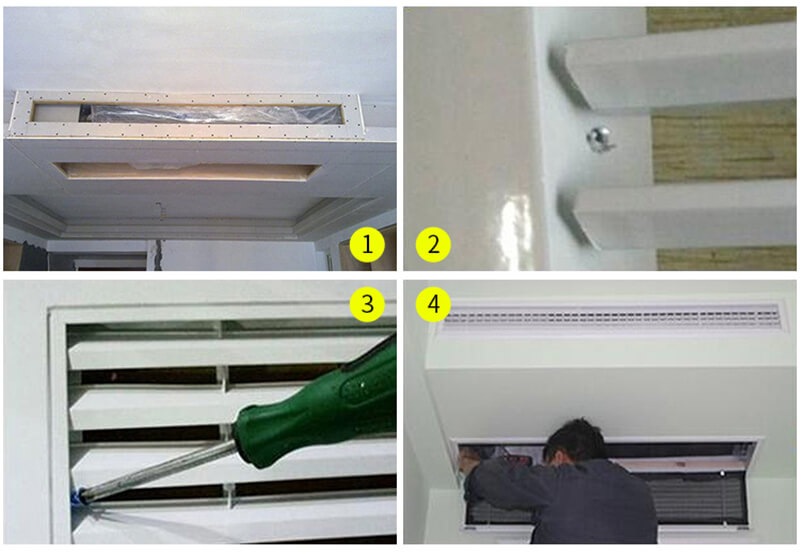

19. Can the Return Air Diffuser Duct be Insulated?
Yes, the ductwork associated with a Return Air Diffuser in an HVAC system can and often should be insulated. Insulating the return air ducts offers several benefits related to energy efficiency, system performance, and overall indoor comfort.
Reasons for Insulating Return Air Ducts
- Energy Efficiency: Insulation helps to maintain the temperature of the air as it travels through the ducts, reducing energy loss and improving the overall efficiency of the HVAC system.
- Preventing Condensation: In certain climates, particularly in areas with high humidity, insulating return air ducts can prevent condensation, which can lead to issues like mold growth or duct corrosion.
- Enhancing Indoor Comfort: By maintaining the temperature of the circulated air, insulation contributes to more consistent indoor comfort levels.
- Noise Reduction: Insulation can dampen the sound of air moving through the ducts, contributing to a quieter environment, especially important in residential settings or noise-sensitive areas.
Types of Duct Insulation
- Fiberglass Insulation: This is a common type of insulation used in HVAC ductwork. It’s often wrapped around the outside of the ducts and can come with a foil backing to act as a vapor barrier.
- Rigid Foam Insulation: Rigid panels of foam insulation can be fitted around ducts for effective thermal insulation.
- Spray Foam Insulation: Spray foam can be applied to the exterior of ductwork and is particularly effective in sealing cracks and gaps.
Considerations for Insulating Return Air Ducts
- Proper Material Selection: Choose insulation materials that are appropriate for the specific HVAC system and climate conditions.
- Thickness of Insulation: The thickness (or R-value) of the insulation should be sufficient to prevent heat loss and meet local building codes.
- Professional Installation: Proper installation is key to ensuring that the insulation is effective. Incorrect installation can lead to reduced efficiency, moisture problems, or even air quality issues.
- Regular Maintenance: Insulated ducts should be periodically inspected for signs of damage or moisture, and to ensure that the insulation remains in good condition.
Insulating return air ducts in an HVAC system is a beneficial practice that enhances energy efficiency, prevents condensation, improves indoor comfort, and reduces noise. The type and thickness of insulation should be carefully selected based on the HVAC system and environmental conditions. Professional installation and regular maintenance are important to ensure the long-term effectiveness of the insulation.
20. What is the difference between Return and Supply Air diffusers?
While both Return and Supply Air Diffusers are crucial for an HVAC system’s functionality, they serve different purposes – return diffusers for air collection and supply diffusers for air distribution. Their design, control mechanisms, and placement within a room or space are tailored to these specific functions, ensuring a balanced and efficient HVAC system.
Return Air Diffusers
- Function:
- Return Air Diffusers are designed to facilitate the movement of air from indoor spaces back to the HVAC system for reconditioning (heating or cooling) and filtration.
- Design Characteristics:
- Typically feature larger openings or grilles to efficiently handle the volume of return air. They are designed to minimize resistance to airflow, ensuring efficient return to the system.
- Generally, have a simpler design as their primary purpose is effective air collection rather than direct air distribution.
- Placement:
- Often strategically located to capture the maximum amount of indoor air and maintain effective circulation. Common placements include central areas or near the floor in some designs.
Supply Air Diffusers
- Function:
- Supply Air Diffusers are used to distribute conditioned air (either heated or cooled) from the HVAC system into the room or space.
- Design Characteristics:
- Usually have adjustable features, like louvers or dampers, to control the direction and spread of the airflow. The design focuses on efficiently dispersing air to maintain comfortable room conditions.
- Can have complex patterns and designs to ensure even distribution and blend with room aesthetics.
- Placement:
- Positioned in areas where conditioned air needs to be effectively dispersed, like under windows, near the floor, or on the ceiling. Placement is key for efficient air distribution and maintaining room comfort.
Key Differences
- Role in HVAC System: Return air diffusers focus on drawing air back into the system for reconditioning, whereas supply air diffusers are responsible for delivering conditioned air into the space.
- Design and Airflow Control: Return diffusers generally have a more passive design, while supply diffusers offer more control over air distribution, direction, and velocity.
- Installation Locations: The placement of return and supply diffusers within a room is typically based on different criteria, with return diffusers positioned to capture the most air and supply diffusers located to best distribute conditioned air.

21. Where Can You Use Return Air Diffuser?
Return Air Diffusers can be used in a wide range of settings, from residential homes to large commercial and industrial buildings. Their placement and specification might vary depending on the specific air circulation and quality needs of each space. Whether in a cozy home environment, a bustling office, or a large public space, return air diffusers play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable, healthy, and well-ventilated environment.
Residential Settings
- Homes and Apartments: In residential buildings, return air diffusers are commonly used in living rooms, bedrooms, and other areas to ensure continuous air circulation back to the HVAC system for heating, cooling, and filtration.
- Basements and Attics: These areas often require effective air circulation to prevent issues like dampness or stagnant air, making return air diffusers necessary.
Commercial and Office Buildings
- Offices and Conference Rooms: To maintain air quality and comfort in workspaces, especially in rooms where many people gather, return air diffusers are essential.
- Lobbies and Common Areas: Large spaces like lobbies benefit from return air diffusers to manage air volume and maintain consistent indoor climates.
Public and High-traffic Areas
- Schools and Universities: Classrooms, lecture halls, and libraries use return air diffusers to handle air circulation effectively, crucial for spaces occupied by many people for extended periods.
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: In these environments, maintaining optimal air quality is critical, and return air diffusers contribute significantly to this requirement.
Industrial and Specialized Settings
- Factories and Warehouses: Such spaces often have specific air quality and circulation needs due to the presence of dust, chemicals, or other pollutants.
- Data Centers: Return air diffusers help manage the temperature and air quality in rooms housing sensitive equipment.
Retail and Hospitality
- Shopping Centers and Stores: Good air circulation is key in these often-crowded spaces for comfort and air quality.
- Hotels and Restaurants: Return air diffusers ensure guest comfort by maintaining consistent temperature and air quality.
Recreational and Leisure Facilities
- Gyms and Indoor Sports Facilities: These spaces require effective air circulation due to high levels of activity and occupancy.
- Theaters and Auditoriums: Consistent air quality and temperature control are vital for audience comfort in these venues.
22. What Quality Standards does the Return Air Diffuser conform to?
Return Air Diffusers are subject to a range of quality standards from bodies like ASHRAE, ISO, UL, and ANSI, as well as energy efficiencies and environmental standards like Energy Star and LEED. Compliance with these standards ensures that the diffusers are safe and effective, and contribute to the overall efficiency and environmental sustainability of HVAC systems. Additionally, adherence to local building codes and manufacturer-specific quality checks further ensures the reliability and performance of these essential HVAC components.
1. ASHRAE Standards
- American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) sets guidelines for HVAC systems, focusing on system performance, indoor air quality, and energy efficiency. Return air diffusers must meet the standards for effective air circulation and filtration as outlined by ASHRAE.
2. ISO Standards
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO): ISO standards, like ISO 7730 and ISO 13779, cover various aspects of HVAC systems, including air quality, environmental impact, and performance criteria.
3. UL Standards
- Underwriters Laboratories (UL): UL standards ensure that HVAC components like return air diffusers are safe to use and meet specific fire safety and electrical safety requirements.
4. ANSI Standards
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI): ANSI standards often collaborate with ASHRAE and other bodies to set unified standards for HVAC systems, including air distribution efficiency and safety.
5. Energy Star Certification
- Although more commonly associated with appliances, Energy Star standards also apply to building materials and components, focusing on energy efficiency. Return air diffusers that conform to Energy Star standards are more energy-efficient, reducing overall energy consumption.
6. LEED Certification
- Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED): While not a standard specifically for diffusers, products used in systems that contribute to a building’s LEED certification need to meet high standards of energy efficiency and environmental impact.
7. Specific Industry Codes
- Building Codes: Local and regional building codes may set additional requirements for HVAC components, including return air diffusers, especially regarding safety, installation, and energy efficiency.
8. Manufacturer-Specific Standards
- Quality Assurance: Reputable manufacturers also adhere to their internal quality standards and testing procedures to ensure their products are reliable and efficient.
The Certifications and Accolades of AIREVERPEAK(Xingsheng):
- National Industrial Products Production License
- European Union CE Certification
- United States Market UL Certification
- ISO 9001 Quality Management System Certification
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management System Certification
- OHSAS 18000 Occupational Health and Safety Certification
- Energy Saving and Low Carbon Certification
- Mechanical and Electrical Equipment Installation Qualification II issued by the Ministry of Construction
- AAA Level Enterprise Recognition
- Jiangsu Famous Brand
- Top 100 Excellent Enterprises in China’s Refrigeration Industry
- Top Ten National Brands in China’s Refrigeration Industry
- Our Air Conditioner Terminal Products Rated as Top Ten Brands in China

Need High-quality HVAC Grilles and Diffusers? Shoot us a message, and I’ll be happy to assist you in picking the right grilles or diffusers for your needs.


