Basic Introduction of HVAC Registers
AIREVERPEAK (XinSheng), your specialized HVAC Registers expert. Renowned for my quality and innovation, I hold prestigious certifications like the national industrial products license, European Union CE, and U.S. market UL. My commitment to excellence is further underscored by ISO certifications in quality, environmental, and occupational health and safety management.
In the HVAC world, I’m a standout with my vast range of over 1000 specification varieties across 26 categories, many of which are recognized as high-tech products. My production approach combines mass assembly, specialization, standardization, and intelligence, ensuring top-notch quality and efficiency. With these capabilities, I’ve become a trusted OEM partner for numerous renowned domestic and international brands and a proud bearer of titles like ‘Top Ten National Brand’ in China’s refrigeration industry.
- Competitive Pricing: Offering competitive prices while maintaining quality is key to attracting both individual and bulk buyers.
- Design Variety: A wide range of styles and finishes allows registers to complement various interior designs.
- Long-lasting Materials: High-quality materials ensure longevity, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Adjustable Designs: Customers value the ability to control air direction and volume, catering to specific room needs.
- Variety of Models: Offering a range of designs and sizes ensures compatibility with different HVAC systems and room layouts.
- Reduced Energy Costs: Well-designed registers can significantly improve the efficiency of an HVAC system, leading to lower energy bills.
HVAC Curved Blade Air Registers
 |  |  |  |
| One Way Register | Two Way Register | Three Way Register | Four Way Register |
HVAC Air Registers
 |  |  |  |
| One Way Register | Two Way Register | Three Way Register | Four Way Register |
HVAC Floor Registers
 |  |  |  |
| Air Register | Floor Register | Victorian Floor Register | Contemporary Steel Floor Register |

If you want to know more, please click below:
- HVAC Linear Slot Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Egg Crate Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Jet Nozzle Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Linear Bar Grilles – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Air Swirl Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Return Air Grille – The Ultimate Guide
HVAC Registers – The Ultimate Guide
1. What are registers in HVAC?
HVAC registers are the grille-covered openings in a building’s walls, floors, or ceilings where air from the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system is delivered into the rooms. They are a visible part of the HVAC system, designed for air distribution and flow control within indoor spaces.
HVAC registers are components in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. They are the grille-like devices you see on walls, ceilings, or floors in various rooms.
2. What are supply registers in HVAC?
Supply registers in HVAC systems are the components responsible for delivering conditioned air from the system into the rooms of a building. They are typically located on walls, ceilings, or floors and feature adjustable slats or louvers. These registers control the direction and flow of air, ensuring efficient distribution of heated or cooled air as required for a comfortable indoor environment.
3. What is the difference between Grill, Register & Diffuser?
Let’s check one video for review:
1. Grills: The Simple Air Passages
- Functionality: Grills, also known as grilles, are basic vent covers that allow air to pass through. They do not have adjustable parts and are used for air supply and return.
- Design: Typically, grills are a simple arrangement of fixed slats or bars and can be found in various shapes and sizes.
2. Registers: The Adjustable Vents
- Added Control: Registers are essentially grills that come with a damper. This addition allows for airflow adjustment, letting you control the volume and direction of air coming through the vent.
- Usage: They are commonly used in areas where variable airflow is necessary. The damper can usually be operated directly on the register with a lever or knob.
3. Diffusers: The Airflow Distributors
- Purpose: Diffusers are used on the supply side of HVAC systems to distribute conditioned air more evenly in a room. They help in spreading the air across a wide area, often in a specific pattern.
- Design Features: Unlike grills and registers, diffusers come in more complex designs that can include vanes or louvers to direct airflow. They are often used in commercial settings and are designed to blend with ceiling tiles or other architectural elements.
Key Differences to Note
Airflow Control and Distribution
- While grills offer no control over airflow, registers allow for adjustment with dampers, and diffusers distribute air more evenly and efficiently across a room.
Application and Placement
- Grills are versatile and can be used for both supply and return air. Registers are typically used in residential settings to supply air where airflow control is needed. Diffusers are more common in commercial applications for an even distribution of air.
Aesthetic and Design Variability
- Grills are the simplest in design and often the most noticeable. Registers can be slightly more complex due to the damper control. Diffusers tend to have the most intricate design, aimed at optimal air distribution and often designed to blend into the ceiling or wall aesthetics.

4. Where do you put HVAC registers?
Correct placement ensures that air is distributed evenly throughout the room, avoiding hot or cold spots and maximizing the comfort and efficiency of the HVAC system. Here’s a guide on where to best place HVAC registers in a building:
1. For Supply Registers:
- Under Windows: Placing supply registers under windows is effective, especially in colder climates, as the incoming warm air combats the cold air descending from the windows.
- Central Room Locations: In rooms without windows or warmer climates, central placement helps distribute air evenly.
2. For Return Registers:
- Opposite Supply Registers: Ideally, return registers should be placed on the opposite side of the room from the supply registers to ensure proper air circulation throughout the space.
- Higher on Walls: Especially in rooms with high ceilings or in climates where cooling is predominant, placing return registers higher on walls helps capture warmer air as it rises.
3. Avoiding Obstructions:
- Away from Furniture: Ensure that registers are not obstructed by furniture, curtains, or other household items to allow free airflow.
- Doors and Walkways: Avoid placing registers in high-traffic areas where they can be blocked or damaged.
4. Considering Room Usage and Layout:
- Bedrooms and Living Areas: In bedrooms, avoid placing registers directly over beds for comfort. In living areas, consider the layout for even air distribution.
- Kitchens and Bathrooms: Due to higher moisture levels, ensure registers are placed to effectively manage humidity and odors.
5. Balancing Aesthetics with Functionality:
- While ensuring functionality, also consider the aesthetic aspect. Registers should blend with the room’s design and not be visually obtrusive.
6. Professional Assessment for Complex Layouts:
- In buildings with complex layouts or specific architectural features, consulting with HVAC professionals can help in determining the optimal placement of registers.

5. How are HVAC registers measured?
1. Measure the Duct Opening:
- Start with the Duct: HVAC registers should be measured based on the size of the duct opening, not the old register or grille.
- Width and Height: Use your tape measure to find the width and height of the duct opening. Measure in inches to ensure accuracy.
2. Record Exact Dimensions:
- Note Down Measurements: Write down the exact measurements of the duct opening. If the measurements fall between sizes, round up to the nearest whole number.
- Double Check: It’s a good practice to measure a second time to confirm accuracy.
3. Understand Sizing Convention:
- Standard Sizing: Registers are often labeled based on the size of the duct they are meant to cover. For instance, a 10″ x 6″ register is designed to fit a 10″ wide by 6″ high duct opening.
4. Account for Faceplate Dimensions:
- Beyond the Duct: Remember, the faceplate of the register will be larger than the duct opening. Ensure enough space around the duct opening to accommodate the register’s faceplate.
5. Consider the Depth of the Register:
- Depth Measurement: In certain installations, the depth of the register might be important, especially if there are obstructions or limited space.
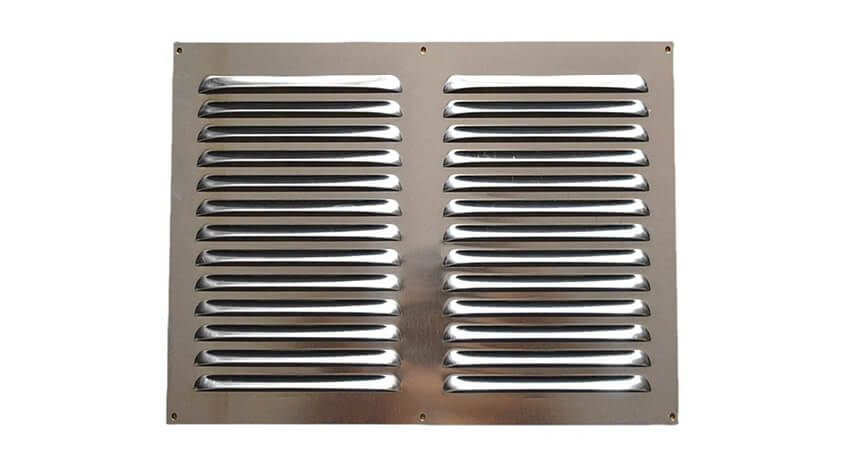

6. What size are HVAC registers?
HVAC registers come in a variety of standard sizes to fit different duct dimensions and airflow requirements. Understanding these standard sizes can help in selecting the right register for your specific needs:
1. Common Dimensions
- Width and Height: HVAC registers are typically measured and categorized by their width and height in inches. Common sizes include 10″ x 6″, 12″ x 6″, 14″ x 8″, and so on, where the first number represents the width and the second number represents the height.
- Duct Opening Size: These dimensions correspond to the size of the duct opening that the register is designed to cover.
2. Custom and Uncommon Sizes
- Custom Options: In addition to standard sizes, custom-sized registers are available for non-standard duct openings. This is particularly useful in older buildings or in cases where unique architectural features dictate specific dimensions.
- Uncommon Sizes: Some buildings might require uncommon sizes due to specific design or airflow needs, and these can often be specially ordered.
3. Depth and Faceplate Dimensions
- Depth: The depth of registers can vary, especially in decorative or specialized designs.
- Faceplate Size: The faceplate of a register is usually larger than the duct opening size to ensure a proper fit and to cover the cutout in the wall or ceiling.
4. Determining the Right Size for Your Needs
- Measure Correctly: To choose the right size, always measure the duct opening rather than the old register or the faceplate.
- Consider Airflow Requirements: The size of the register should align with the HVAC system’s airflow needs to maintain efficiency and comfort.
7. How do HVAC registers work?
1. Airflow Direction and Control:
- Adjustable Slats: Registers are equipped with a series of adjustable slats or vanes. These can be manually positioned to direct the airflow either up, down, or to the sides, according to the specific needs of the room.
- Volume Regulation: Apart from direction, the slats can also be adjusted to control the volume of air passing through the register, allowing for increased or decreased airflow.
2. Integration with Ductwork:
- The endpoint of HVAC Ducts: Registers are located at the end of HVAC ductwork, serving as the final exit point for conditioned air into the room.
- Dual Role: Besides allowing air into a room, they also facilitate the return of air back to the HVAC system for reconditioning, maintaining a continuous air circulation cycle.
3. Enhancing Indoor Comfort:
- Balanced Air Distribution: By adjusting the registers, it’s possible to achieve a balanced distribution of air, avoiding issues like hot or cold spots in a room.
- Customizable Comfort: Users can personalize their indoor environment by changing the direction and volume of airflow to suit their comfort levels.

8. How many HVAC registers per room?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer to how many HVAC registers are needed per room, as it depends on various factors like room size, system capacity, and specific ventilation needs. Accurately assessing these aspects will help determine the right number of registers to ensure efficient air distribution and maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
1. Room Size and Layout:
- Square Footage: A fundamental factor in determining the number of registers is the size of the room. Larger rooms typically require more registers to ensure even air distribution.
- Room Configuration: The layout of the room, including the placement of doors, windows, and interior walls, can affect airflow and may influence the number of registers needed.
2. HVAC System Capacity:
- System Output: The capacity of your HVAC system also plays a role. Systems designed to output more air may require more registers to distribute this air effectively throughout the space.
3. Air Exchange Rates:
- Ventilation Needs: Different types of rooms have varying air exchange requirements. For example, kitchens and bathrooms might need more registers due to higher moisture and odor levels.
4. Ceiling Height:
- Vertical Space: High ceilings can affect how air circulates in a room. Rooms with higher ceilings might require additional registers to circulate air adequately.
5. Local Building Codes and Standards:
- Regulatory Requirements: It’s important to check local building codes, as they often have specific guidelines on ventilation requirements that can dictate the number of registers per room.
6. Professional Assessment:
- Consulting with HVAC professionals is recommended, especially for complex spaces. They can provide a detailed assessment based on room dynamics and system specifications.
9. What is the main function of registers?
1. Controlling Airflow:
- Volume Adjustment: Registers are equipped with dampers or adjustable slats that allow you to control the volume of air flowing through them. This adjustability is crucial for regulating the amount of heated or cooled air entering a room.
- Customizable Comfort: By controlling the airflow, registers enable individuals to customize the climate within their space, enhancing overall comfort.
2. Directing Airflow:
- Strategic Air Distribution: Registers are designed to direct airflow in specific directions. This can be towards or away from certain areas in the room, depending on the desired air distribution pattern.
- Preventing Drafts: Properly adjusted registers can help avoid direct drafts, evenly distribute air, and maintain consistent room temperatures.
3. Integrating with HVAC System:
- End Point of Ductwork: Registers serve as the terminal points of an HVAC system’s ductwork, functioning as the interface between the ducts and the indoor environment.
- Efficiency in Circulation: They play a key role in ensuring efficient circulation of air, crucial for the HVAC system’s overall effectiveness.
4. Enhancing Room Aesthetics:
- Decorative Elements: Beyond functionality, registers can also contribute to a room’s aesthetic appeal. They come in various styles and finishes to complement different interior designs.
10. What is the difference between a duct and a register?
While both ducts and registers are integral to an HVAC system, they serve different purposes. Ducts act as the hidden transportation channels for air, and registers serve as the controllable outlets that deliver air into a room:
Understanding the Roles of Ducts and Registers
1. The Function of Ducts:
- Air Transport Channels: Ducts are the conduits or passageways that transport air throughout the HVAC system. They are typically made of sheet metal, fiberglass, or other durable materials and are hidden within walls, floors, or ceilings.
- System Backbone: Serving as the circulatory system of HVAC, ducts carry conditioned air (heated or cooled) from the HVAC unit to various parts of the building and return spent air back to the system for reconditioning.
2. The Role of Registers:
- Airflow Control and Delivery: Registers are the visible grilles or covers located at the end of ducts. They allow the conditioned air to exit the ducts and enter the living or working space.
- Adjustability for Comfort: Unlike simple grilles, registers usually come with movable louvers or dampers, allowing occupants to adjust the direction and volume of airflow for personalized comfort.
Key Differences Between Ducts and Registers
Material and Construction:
- Ducts are often constructed from metal, fiberglass, or other materials suitable for long air transport channels. Registers are typically made of metal or plastic and are designed for durability and ease of use.
Location and Visibility:
- Ducts are mostly hidden within the structure of a building, while registers are visible and accessible to the occupants, usually mounted on walls, ceilings, or floors.
Functionality:
- Ducts are passive elements, simply serving as pathways for air. On the other hand, Registers offer active control over the airflow, allowing adjustments for better air distribution and room comfort.

11. How many types of HVAC registers are in HVAC?
1. Floor Registers:
- Design: Typically have a grille design for durability to withstand foot traffic.
- Placement: Installed on the floor, they are ideal for distributing heat as warm air rises, making them effective for heating systems.
2. Ceiling Registers:
- Features: Often come with adjustable louvers for directing airflow.
- Usage: Common in central air conditioning systems, they are placed in ceilings to distribute cool air, which naturally descends.
3. Wall Registers:
- Construction: Similar to ceiling registers but designed for wall installation.
- Function: Used for both heating and cooling systems, wall registers can help distribute air evenly throughout the room.
4. Baseboard Registers:
- Appearance: Usually taller and narrower than other types, fitting seamlessly along the baseboard.
- Application: Effective for heating, especially in rooms with large windows, as they help counteract the cold air descending from the glass.
5. Toe-Kick Registers:
- Design: Small and discreet, designed to fit into the toe-kick spaces under cabinets.
- Ideal for: Kitchens and bathrooms, where they can provide heating without taking up wall or floor space.
6. Return Air Registers:
- Purpose: Specifically designed for returning air to the furnace or air handler for reconditioning.
- Characteristics: Lack adjustable louvers and are larger than supply registers to handle the higher volume of return air.
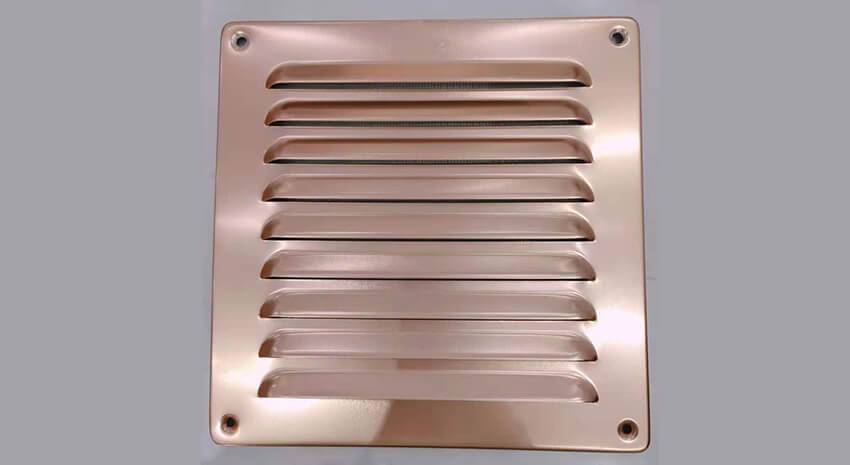

12. What material are the HVAC registers?
HVAC registers, an essential component of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, are made from a variety of materials. Each material offers different benefits in terms of durability, aesthetics, and functionality. Knowing what materials are commonly used for HVAC registers can guide you in choosing the right type for your specific needs:
1. Aluminum: Lightweight and Durable
- Characteristics: Aluminum registers are known for their lightweight, strength, and resistance to corrosion.
- Advantages: They are easy to handle and install, and their rust-resistant nature makes them suitable for humid areas like bathrooms and kitchens.
2. Steel: Robust and Sturdy
- Attributes: Steel registers are heavier and sturdier than aluminum, making them durable and long-lasting.
- Applications: Ideal for high-traffic areas or industrial settings where strength is a priority.
3. Stainless Steel: Sleek and Corrosion-Resistant
- Benefits: Stainless steel registers offer a sleek, modern look and are highly resistant to rust and corrosion.
- Usage: Common in commercial and contemporary residential settings, they are particularly useful in coastal areas where saltwater can cause corrosion.
4. Plastic: Versatile and Cost-Effective
- Features: Plastic registers are lightweight and can come in various colors and styles. They are rustproof and often more affordable than metal registers.
- Suitability: Perfect for budget-conscious projects and low-humidity environments.
5. Wood: Aesthetic and Natural
- Appearance: Wooden registers provide a warm, natural look and can be painted or stained to match flooring or furniture.
- Considerations: More suited for decorative purposes, they are typically used in residential settings where blending with interior decor is desired.
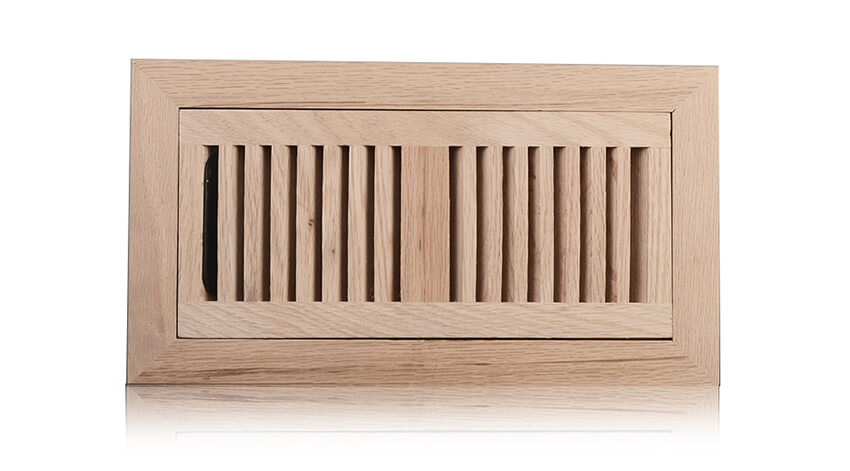

13. What are the advantages of HVAC registers?
HVAC registers are a vital component in any climate control system, offering several functional advantages that enhance the overall performance and comfort provided by HVAC systems. They provide essential control over airflow, contribute to energy efficiency, integrate aesthetically with interior designs, aid in maintaining indoor air quality, and are built for durability.
Advantages of Using HVAC Registers
1. Airflow Control:
- Directional Adjustment: Registers allow for the control of airflow direction within a space. By adjusting the louvers, air can be directed upward, downward, or to the sides as needed, enhancing comfort levels in different areas of a room.
- Volume Regulation: The ability to control the volume of air flowing through the registers helps in maintaining the desired temperature and airflow, contributing to a more comfortable environment.
2. Enhanced Energy Efficiency:
- Improved Air Distribution: Properly adjusted registers promote efficient air distribution, reducing the need for HVAC systems to work harder to heat or cool a space. This can lead to energy savings and lower utility bills.
3. Aesthetic Integration:
- Design Variety: HVAC registers come in various styles and finishes, allowing them to blend seamlessly with different interior designs. This aesthetic versatility ensures that functionality does not come at the cost of style.
- Complements Decor: Whether the setting is residential or commercial, the right register design can complement the overall decor and contribute to the room’s visual appeal.
4. Indoor Air Quality Improvement:
- Dust and Debris Reduction: Registers can help in reducing the amount of dust and debris entering the air stream, especially when equipped with filters, thus improving indoor air quality.
5. Easy Maintenance:
- Accessibility for Cleaning: Registers are typically designed for easy removal or access, making them convenient to clean and maintain. Regular cleaning of registers is essential for optimal system performance and air quality.
6. Durability and Longevity:
- Sturdy Construction: Made from materials like aluminum, steel, or plastic, registers are durable and can withstand long-term use without significant wear, ensuring the longevity of the HVAC system’s components.
14. How is an HVAC register Installation Process?
1. Preparation and Safety:
- Gather Tools: Ensure you have all the necessary tools, including a screwdriver, measuring tape, and the HVAC register.
- Turn Off HVAC System: Before beginning the installation, turn off your HVAC system to ensure safety and prevent dust or debris from circulating.
2. Measure and Inspect the Duct Opening:
- Accurate Measurement: Measure the duct opening where the register will be installed. Ensure that the dimensions match the size of the register you have.
- Inspect for Damage: Check the duct opening for any damage or irregularities. Any issues should be addressed before installing the new register.
3. Positioning the Register:
- Align the Register: Carefully place the register over the duct opening, making sure it fits snugly and is properly aligned.
- Secure in Place: Most registers come with pre-drilled holes and mounting screws. Use these to fasten the register to the duct opening securely.
4. Adjusting the Louvers:
- Test Airflow Direction: Adjust the louvers to direct airflow in the desired direction. This can be done manually on most register models.
5. Final Checks:
- Ensure a Tight Fit: Double-check that the register is securely fastened and there are no gaps around the edges.
- Operational Test: Turn the HVAC system back on and observe the airflow through the new register to ensure it is functioning as expected.
6. Ongoing Maintenance:
- Regular Cleaning: Keep the register clean and free of dust to maintain optimal airflow and system efficiency.

15. How do I choose an HVAC register?
Selecting the right HVAC register involves balancing functionality with aesthetic appeal. Consider the size, airflow requirements, material, design, and energy efficiency to find a register that fits both your practical needs and style preferences.
Factors to Consider in Choosing an HVAC Register
1. Size and Fit:
- Measure the Duct Opening: Before purchasing a register, accurately measure the duct opening. The register needs to fit these dimensions for proper installation.
- Consider the Depth: Besides the length and width, also take into account the depth of the register, especially if there are obstructions near the duct opening.
2. Airflow Requirements:
- Room Size and Usage: Consider the size of the room and how it’s used. Larger rooms or those with high ceilings may require registers with greater airflow capacity.
- Airflow Direction: Decide if you need a register with adjustable louvers for directional control of air. This is particularly important in living spaces, where you want to avoid direct drafts.
3. Material and Durability:
- Material Options: Registers are commonly made from materials like aluminum, steel, or plastic. Choose a material based on durability, maintenance needs, and the environmental conditions of your space.
- Corrosion Resistance: In areas with high humidity or moisture, like bathrooms, consider rust-resistant materials.
4. Aesthetic Considerations:
- Style and Finish: Registers come in various designs and finishes. Select a style that complements your room’s decor and fits the overall aesthetic of your home or office.
- Color Matching: Consider the color of your floors, walls, and furniture. Many registers can be painted to match your interior design.
5. Energy Efficiency:
- Energy Impact: The right register can contribute to the energy efficiency of your HVAC system by facilitating proper airflow and reducing the system’s workload.
6. Noise Level:
- Noise Reduction: Some registers are designed to minimize noise when air passes through them. This could be a crucial factor in bedrooms or quiet spaces.
16. What temperature should HVAC be at the register?
Temperature Differences are normal for the temperature at the register to be different from the set thermostat temperature. This is due to the cooling or heating process and the distance air travels through ductwork.
Ideal Temperatures for Cooling and Heating:
- Cooling Season: During summer or in warmer climates, the air from AC registers typically should be around 15-20 degrees cooler than the room’s desired temperature.
- Heating Season: In winter or colder climates, air from heating registers should be about 15-20 degrees warmer than the room’s target temperature.
Factors Affecting Register Temperature:
- Ductwork Insulation: Poorly insulated ducts can lead to significant temperature loss, especially in unconditioned spaces like attics or basements.
- System Efficiency: Older or poorly maintained HVAC systems may not reach the ideal temperature differential at the registers.
Monitoring and Adjusting Temperatures:
- Use a Thermometer: To check the temperature, hold a thermometer near the register and compare the reading with your thermostat setting.
- Adjustments: If there’s a significant discrepancy, it might indicate a need for system maintenance, ductwork insulation improvements, or adjustments to the thermostat setting.

17. Should HVAC registers be on the floor or ceiling?
Choosing between floor and ceiling HVAC registers depends on various factors including climate, the primary use of the HVAC system (heating vs. cooling), room layout, and personal preferences. In cold climates or for systems primarily used for heating, floor registers might be preferable. Conversely, in warm climates or for cooling-centric systems, ceiling registers may offer better efficiency:
Floor vs. Ceiling HVAC Registers: Pros and Cons
1. Floor Registers: Advantages and Considerations
- Heat Distribution: Since hot air rises, floor registers are often effective for heating. They allow warm air to rise naturally, providing even heat distribution, especially in cold climates.
- Accessibility: Floor registers are typically easier to access for cleaning and maintenance.
- Room Layout Restrictions: Furniture and floor coverings can obstruct airflow from floor registers. It’s essential to place them strategically to avoid blockages.
2. Ceiling Registers: Benefits and Factors
- Cool Air Distribution: In climates where cooling is the primary concern, ceiling registers are advantageous. Cool air descends from the ceiling, spreading evenly across the room.
- Space Saving: Ceiling registers are less likely to be obstructed by furniture, offering more flexibility in room layout and interior design.
- Aesthetic Impact: Ceiling registers can be more discreet and less noticeable than floor registers, blending seamlessly into the ceiling.
3. Climate Considerations
- Cold Climates: In areas with longer heating seasons, floor registers might be more efficient for heat distribution.
- Warm Climates: For places where air conditioning is used more frequently, ceiling registers can provide more effective cooling.
4. Type of HVAC System
- The choice between floor and ceiling registers also depends on the type of HVAC system installed. Systems designed for specific air delivery methods may require one placement over the other.
5. Energy Efficiency and Comfort
- Properly placed registers, whether on the floor or ceiling, contribute to the energy efficiency of the HVAC system. Efficient air distribution means the system doesn’t have to work as hard to maintain the desired temperature.

18. What is the difference between a floor vent and a register?
The main difference between floor vents and registers lies in their functionality. Floor vents are basic grilles that allow air to pass through, while registers are equipped with mechanisms for controlling and directing airflow.
Comparing Floor Vents and Registers
1. The Role of Floor Vents:
- Basic Function: Floor vents are essentially openings or grilles placed on the floor, designed to allow air from the HVAC system into a room. They are passive components without adjustable features.
- Design: Typically, floor vents are a simple grille design made to cover the duct opening on the floor. They can come in various materials and styles but do not have moving parts.
2. The Functionality of Registers:
- Airflow Control: Registers, on the other hand, are advanced versions of vents that come equipped with dampers or adjustable louvers. This feature allows control over the direction and volume of airflow.
- Adjustable Design: Registers offer the flexibility to modulate airflow, which can be adjusted to suit the comfort needs of the room’s occupants. The dampers can be manually adjusted to open or close the air passage to a desired extent.
Key Differences Between Floor Vents and Registers
Control and Customization:
- The primary difference lies in control. Floor vents simply cover duct openings and allow air to pass through, whereas registers offer the ability to adjust and direct the airflow as per requirement.
Usage and Efficiency:
- Registers are more versatile and efficient in managing room temperature and airflow, making them suitable for areas where more precise air control is desired.
- Floor vents are more suitable for areas where simple air passage is sufficient and customization of airflow is not a priority.
Aesthetic and Structural Variations:
- While both floor vents and registers can vary in design and material, registers often offer more variety due to their functional complexity.
- The choice between a vent and a register can also be influenced by aesthetic preferences and the specific interior design of a space.

Need High-quality HVAC Grilles and Diffusers? Shoot us a message, and I’ll be happy to assist you in picking the right grilles or diffusers for your needs.


