The Certifications and Accolades of AIREVERPEAK(Xingsheng):
- National Industrial Products Production License
- European Union CE Certification
- United States Market UL Certification
- ISO 9001 Quality Management System Certification
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management System Certification
- OHSAS 18000 Occupational Health and Safety Certification
- Energy Saving and Low Carbon Certification
- Mechanical and Electrical Equipment Installation Qualification II issued by the Ministry of Construction
- AAA Level Enterprise Recognition
- Jiangsu Famous Brand
- Top 100 Excellent Enterprises in China’s Refrigeration Industry
- Top Ten National Brands in China’s Refrigeration Industry
- Our Air Conditioner Terminal Products Rated as Top Ten Brands in China
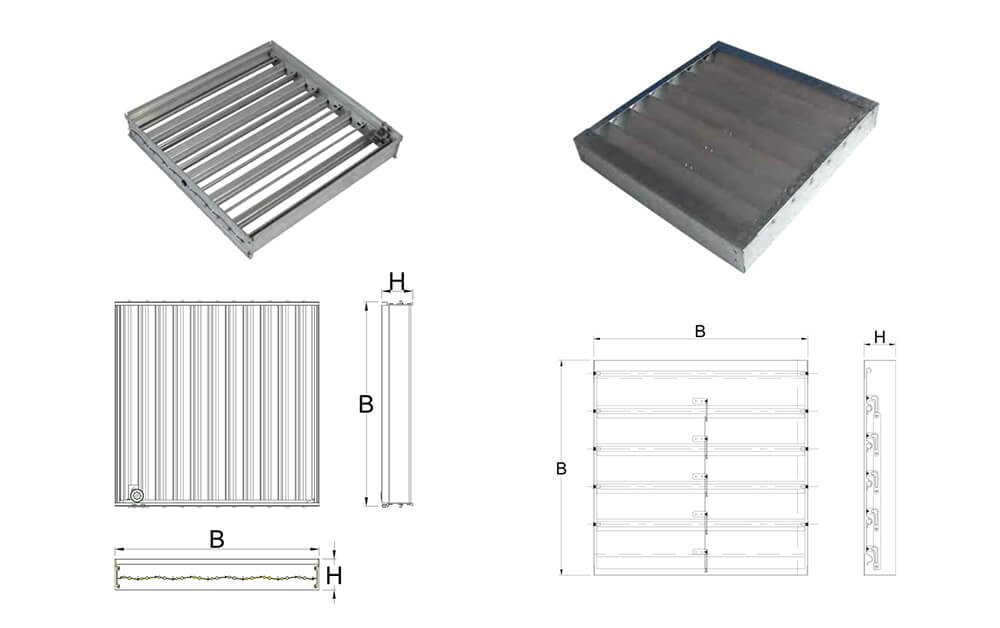
Basic Introduction of HVAC Damper
- Advanced Materials: The use of long-lasting, corrosion-resistant materials ensures durability and reliability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Emphasize the long-term savings due to energy efficiency and durability, which are key considerations for businesses.
- Customization and Flexibility: The ability to customize dampers for specific architectural or environmental needs is a significant advantage in commercial projects.
- Technical Support and Warranty: Offering robust customer support and warranty options can be a major selling point.
- Bulk Purchase Options: Offering competitive pricing for bulk orders can attract larger projects and repeat business.
- After-Sales Support: Offering excellent after-sales service can differentiate your brand and build long-term customer relationships.
Feature Description
- Adjustable (Optional)
- Mill finish or anodized or powder-coated
- Size can be customized
- Made of aluminum profile 6063 T5
- Dimensions tolerance is ± 1mm or ± 2mm (as the styles)
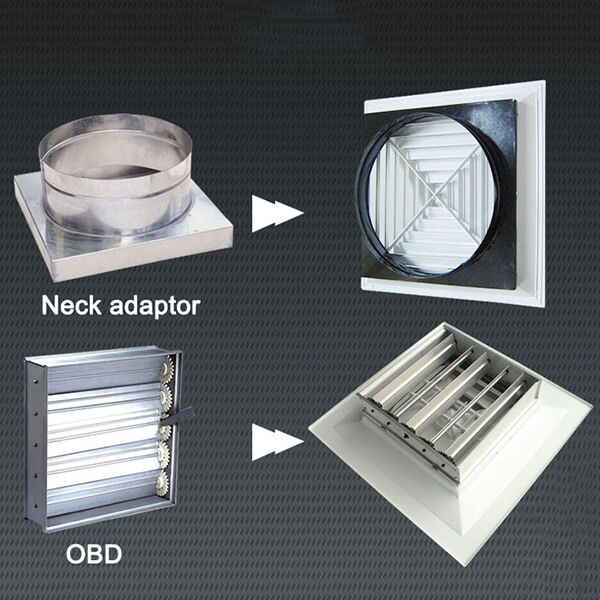
- The frame is made of galvanized steel 0.8mm thick (as the style)
- The barrel is made of galvanized steel 0.6mm thick (Optional)
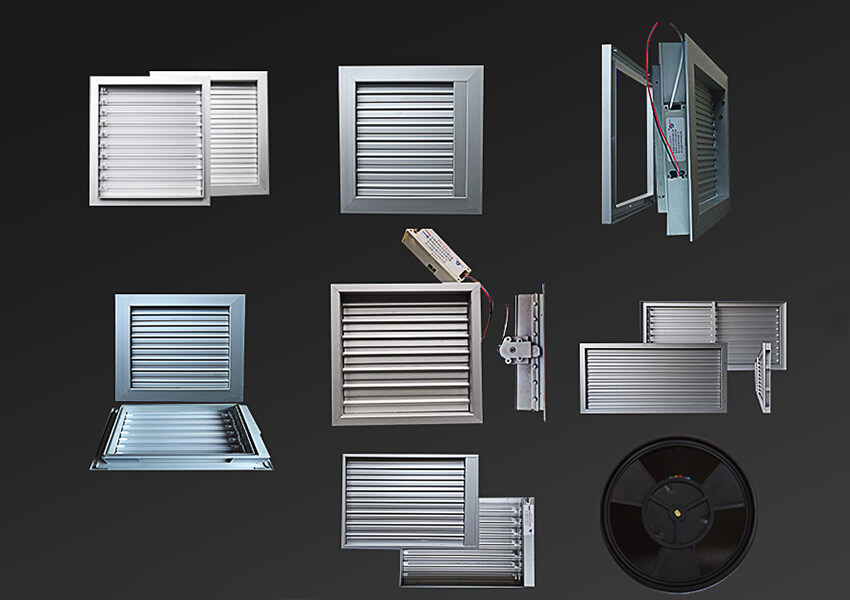
Basic styles and sizes of HVAC Damper

If you want to know more, please click below:
- HVAC Linear Slot Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Egg Crate Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Jet Nozzle Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Linear Bar Grilles – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Air Swirl Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Return Air Grille – The Ultimate Guide
- Exhaust Air Louver – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Registers – The Ultimate Guide
HVAC Damper – The Ultimate Guide
1. What is an HVAC damper?
An HVAC damper is a component in your heating, ventilation, and air conditioning system. Its main job is to control the flow of air through the ducts in your home. Think of it like a valve that can open and close to let more or less air through.
Dampers are found in the ductwork and can be adjusted either manually or automatically. Manual dampers have a handle or lever you can move to control the airflow. Automatic dampers are connected to your HVAC system’s controls, and they adjust themselves based on the temperature you set for each room.
In simple terms, HVAC dampers help make sure that each room in your house gets the right amount of heated or cooled air. This makes your HVAC system more efficient and keeps your home comfortable.
2. How do HVAC dampers work?
HVAC dampers function by regulating and controlling the flow of air within the ductwork of a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system.
Mechanism of Operation
- Blades or Louvers: HVAC dampers consist of blades or louvers. These components can rotate or slide to open or close, thereby controlling the passage of air through the duct.
- Adjustment of Airflow: When the damper blades are in an open position, air flows freely through the duct. Conversely, when the blades are closed, they restrict or completely block the airflow.
- Manual or Motorized Control: Dampers can be manually adjusted or controlled via a motorized mechanism. Manual dampers require physical adjustment, whereas motorized dampers are controlled by electric or pneumatic motors, often as part of an automated HVAC system.
- Zone Control Functionality: In systems with zoning capabilities, dampers control airflow to specific areas or ‘zones’. This allows for differentiated temperature control across various sections of a space, enhancing comfort and efficiency.
- Thermostat or Central System Integration: In automated systems, dampers are often connected to thermostats or a central control system. They adjust the airflow in response to the temperature demands set by these controls, ensuring the desired climate conditions in different areas.

3. What are the different types of HVAC dampers available?
The different types of HVAC dampers include manual dampers, motorized dampers, volume control dampers, zone dampers, fire dampers, smoke dampers, backdraft dampers, balancing dampers, and butterfly dampers. Each type serves a specific purpose, from basic airflow regulation to safety functions like preventing the spread of fire and smoke.
Manual Dampers
- Basic Operation: These dampers are adjusted by hand and are typically used to balance airflow in the system. They are simple in design and do not require external power.
Motorized Dampers
- Automated Control: Motorized dampers are operated by electric or pneumatic motors. They can be programmed or controlled remotely, often as part of an automated HVAC system.
Volume Control Dampers (VCD)
- Regulate Air Volume: Used to control the volume of air passing through the duct. VCDs are effective in regulating airflow to maintain consistent temperatures in different zones.
Zone Dampers
- Individual Zone Control: Designed for systems with zoning capabilities, zone dampers control airflow to specific areas, allowing for individualized temperature control across different rooms or zones.
Fire Dampers
- Safety Feature: Fire dampers are safety devices that close automatically in the event of a fire to prevent the spread of flames and smoke through the ductwork.
Smoke Dampers
- Prevent Smoke Spread: Similar to fire dampers, smoke dampers are designed to block the passage of smoke through the ducts. They can be triggered by smoke detectors or fire alarm systems.
Backdraft Dampers
- Prevent Reverse Airflow: These dampers prevent air from flowing backward through the system, crucial in exhaust and ventilation applications.
Balancing Dampers
- Fine-Tuning Airflow: Installed to fine-tune the airflow in specific areas, balancing dampers are used for minor adjustments to ensure even distribution of air.
Butterfly Dampers
- Simple and Efficient Design: Characterized by their round, butterfly-wing-like blades, these dampers are used for quick and effective airflow control, especially in round ducts.

4. How do I choose the right HVAC damper for my system?
Choosing the right HVAC damper involves understanding your system’s needs, determining the damper’s purpose, considering zone control requirements, evaluating ductwork configuration, deciding on the type of operation, ensuring compatibility with existing controls, focusing on energy efficiency, assessing material quality, adhering to safety and building codes, and seeking professional advice. Careful consideration of these factors will ensure the selection of an appropriate damper that enhances the functionality and efficiency of your HVAC system.
Understand Your HVAC System’s Needs
- Assess System Type and Size: Consider the type and size of your HVAC system. Larger systems or those with complex zoning might require more sophisticated dampers like motorized or zone dampers.
Determine the Purpose of the Damper
- Airflow Control or Safety: Decide whether the damper is primarily for controlling airflow or for safety purposes. For general airflow management, volume control or balancing dampers are suitable. For fire safety, fire or smoke dampers are necessary.
Consider Zone Control Requirements
- Individual Room Control: If your system includes, or you plan to include, HVAC zoning for individual room control, opt for zone dampers. These allow you to control the temperature in different areas independently.
Evaluate the Ductwork Configuration
- Duct Shape and Size: Choose a damper that fits the shape and size of your ductwork. For round ducts, butterfly dampers are often ideal, while rectangular ducts may require a different style.
Type of Damper Operation
- Manual vs. Motorized: Decide between manual and motorized dampers. Manual dampers are simpler and more cost-effective but require manual adjustment. Motorized dampers offer automated control and are better suited for complex systems or remote operations.
Check for Compatibility with Existing Controls
- Integration with HVAC Controls: Ensure the damper is compatible with your existing HVAC control system, especially if you’re considering automated or motorized dampers.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
- Impact on System Efficiency: Consider how the damper will affect your system’s energy efficiency. Properly selected and installed dampers can reduce energy costs by optimizing airflow and temperature control.
Material and Quality
- Durability and Performance: Select dampers made from high-quality, durable materials to ensure long-term performance and reduce the need for frequent replacements or repairs.
Safety and Building Code Compliance
- Regulatory Standards: Ensure the damper meets all relevant safety and building codes, especially fire and smoke dampers, which must comply with strict safety regulations.
Professional Advice
- Consult with HVAC Experts: If unsure, consult with an HVAC professional. Their expertise can guide you in choosing the right damper for your specific system and needs.
5. Can HVAC dampers help in improving air quality?
Yes. HVAC dampers contribute to improved indoor air quality by optimizing air distribution, supporting zoned systems for customized environmental control, preventing air stagnation, assisting with humidity control, complementing air filtration systems, and reducing the spread of contaminants. While dampers themselves do not clean or filter the air, their role in effective air management is essential for maintaining a healthy indoor air environment.
Regulating Airflow for Balanced Ventilation
- Optimized Air Distribution: By adjusting the airflow in different parts of the building, HVAC dampers help ensure that fresh, conditioned air is evenly distributed. Balanced ventilation is crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality.
Supporting Zoned HVAC Systems
- Customized Environmental Control: In zoned HVAC systems, dampers allow for individualized control over the heating, cooling, and ventilation in different areas. This can be especially beneficial in maintaining IAQ in areas with specific air quality needs.
Preventing Stagnant Air
- Reducing Air Stagnation: Proper use of HVAC dampers can prevent stagnant air in certain areas of a building. Stagnant air can lead to higher concentrations of pollutants; thus, its prevention is key to maintaining healthy indoor air.
Assisting with Humidity Control
- Managing Moisture Levels: By regulating airflow, dampers can indirectly help in controlling humidity levels in indoor spaces. Balanced humidity is vital for preventing mold growth and maintaining a comfortable indoor environment.
Complementing Air Filtration Systems
- Enhanced Filtration Efficiency: While dampers themselves do not filter air, they can be used in conjunction with HVAC systems that have air filtration components. Proper airflow regulation ensures that air passes effectively through filters, thereby removing contaminants more efficiently.
Reducing Contaminant Spread
- Isolating Areas: In scenarios like cooking odors or temporary indoor pollutants, dampers can be adjusted to isolate certain areas to prevent the spread of contaminants throughout the building.

6. What is the difference between manual and automatic dampers?
The main differences between manual and automatic dampers lie in their mode of operation, control mechanisms, usage, and flexibility. Manual dampers are hand-operated, maintain a fixed setting, and are suitable for simpler, cost-effective applications. In contrast, automatic dampers are motor-operated, respond to changing conditions, and are ideal for complex HVAC systems with variable airflow needs.
Manual Dampers
- Operation – Hand-Operated: Manual dampers are adjusted by hand. They typically have a lever or handle that is used to open or close the damper blades.
- Control – Fixed Setting: Once set, manual dampers maintain the same position until manually adjusted again. They do not respond to changes in temperature or air pressure.
- Usage – Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness: They are often used in simpler HVAC systems where constant airflow regulation is not required. Manual dampers are more cost-effective due to their basic design.
- Flexibility – Limited Adjustability: Manual dampers are less flexible in terms of automatic adjustments for changing conditions within the HVAC system.
Automatic Dampers (Motorized Dampers)
- Operation – Powered by Motors: Automatic dampers are operated by electric or pneumatic motors. They can open and close in response to signals from a control system.
- Control – Responsive Adjustment: These dampers can automatically adjust their positions based on the HVAC system’s requirements, such as changes in temperature, air pressure, or system demands.
- Usage – Complex Systems and Zoning: They are ideal for more complex HVAC systems, especially those with zoning capabilities, where airflow needs to vary in different areas of a building.
- Flexibility – High Adjustability: Automatic dampers offer greater flexibility and precision in controlling airflow, and adapting to the building’s changing environmental conditions.

7. How often do HVAC dampers need maintenance or replacement?
HVAC dampers generally require annual maintenance, but this can vary based on the damper type, system usage, and environmental conditions. Regular checks help identify wear and tear, operational issues, or noise problems that indicate maintenance or replacement needs. The average lifespan of dampers can be around 10 to 15 years, although this is influenced by several factors.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
- Routine Checks: HVAC dampers should be inspected at least annually as part of a broader HVAC system maintenance routine. This helps identify any issues before they escalate.
Factors Influencing Maintenance Frequency
1. Type of Damper
- Manual vs. Automatic: Manual dampers generally require less frequent maintenance than automatic dampers, which have more complex components like motors and control systems.
2. System Usage
- High vs. Low Use: Dampers in systems that are heavily used or in large commercial settings may need more frequent checks and maintenance compared to those in smaller or less frequently used systems.
3. Environmental Conditions
- Harsh Environments: Dampers exposed to harsh conditions, such as high humidity, dust, or corrosive environments, may require more frequent maintenance.
Signs Indicating Maintenance or Replacement
- Wear and Tear: Visible signs of wear, such as rust or corrosion on metal dampers, can indicate the need for maintenance or replacement.
- Operational Issues: Difficulty in adjusting manual dampers or malfunctioning motorized dampers are signs that maintenance is required.
- Noise: Unusual noises during operation may suggest that dampers need servicing.
Replacement Considerations
- Lifespan of Dampers: The average lifespan of HVAC dampers varies but can range from 10 to 15 years. This can be shorter or longer depending on usage and environmental conditions.
- Upgrading System: Consider replacing dampers when upgrading the HVAC system for improved efficiency or compatibility with new system components.
Professional Assessment
- Expert Inspection: Having a professional HVAC technician inspect and service the dampers can provide a more accurate assessment of their condition and functionality.
8. Can I install an HVAC damper myself, or do I need a professional?
Let’s watch a video for review:
Whether you can install an HVAC damper yourself depends on your skill level, familiarity with your HVAC system, and the complexity of the damper and system. For basic manual dampers and straightforward systems, a DIY approach might be feasible. However, for more complex installations, especially with motorized dampers in sophisticated systems, professional installation is recommended to ensure safety, efficiency, and compliance with regulations and warranties.
DIY Installation
1. Consider Your Skill Level
- Basic Mechanical Skills Required: If you have a good understanding of HVAC systems and basic mechanical skills, you may be able to install certain types of dampers, like manual dampers, yourself.
2. Understanding System Requirements
- Familiarity with Your HVAC System: Successful DIY installation requires a thorough understanding of your system’s layout and airflow requirements. This includes knowing where the damper needs to be placed for optimal effectiveness.
3. Safety Precautions
- Adherence to Safety Standards: Safety is paramount. Ensure you can safely access the installation location and are familiar with necessary safety precautions, including turning off the HVAC system before beginning work.
Professional Installation
1. Complex Systems and Motorized Dampers
- Expertise for Advanced Systems: For complex HVAC systems or when installing motorized dampers, professional installation is recommended. These systems often require precise calibration and integration with existing controls that are best handled by a technician.
2. Ensuring Correct Installation
- Avoiding Future Problems: Incorrectly installed dampers can lead to inefficiencies, increased wear and tear on the system, and even safety hazards. Professionals ensure that dampers are installed correctly, avoiding these issues.
3. Compliance with Codes
- Building and Safety Regulations: A professional installer will ensure that the installation complies with all relevant building codes and safety standards.
Tools and Equipment
- Access to Proper Tools: Professional installers have the necessary tools and equipment to install dampers efficiently and safely, which might not be readily available to the average homeowner.
Warranty Considerations
- Avoiding Warranty Issues: DIY installation may void certain warranties on your HVAC system or the damper itself. Professional installation helps maintain these warranties.
9. How do HVAC dampers affect energy efficiency?
HVAC dampers contribute to energy efficiency by optimizing airflow distribution, enhancing zone control, preventing air leakage, efficiently managing temperature, reducing the load on air handlers, supporting energy recovery systems, and enabling automated energy-saving adjustments. Their role in effectively controlling and managing airflow is essential in reducing unnecessary energy consumption and enhancing the overall efficiency of HVAC systems.
Optimized Airflow Distribution
- Balanced Ventilation: By regulating airflow within the ductwork, HVAC dampers ensure that air is distributed evenly throughout the building. This balanced distribution reduces the need for the system to overwork, thereby saving energy.
Enhanced Zone Control
- Targeted Heating and Cooling: In systems with zoning capabilities, dampers allow for precise control of air delivery to different zones. This means heating or cooling can be concentrated where it’s needed, reducing energy wastage in unoccupied areas.
Preventing Air Leakage
- Maintaining System Integrity: Properly functioning dampers help maintain the integrity of the HVAC system by preventing air leaks. Minimizing air leakage is key to maintaining system efficiency and reducing energy consumption.
Reducing Overheating and Overcooling
- Efficient Temperature Management: Dampers play a crucial role in managing the temperatures within different areas of a building. This helps avoid scenarios where certain areas become overheated or overcooled, leading to unnecessary energy expenditure.
Improved Air Handler Efficiency
- Reduced Load on Air Handlers: By controlling airflow effectively, dampers can reduce the load on air handlers and other HVAC equipment. This not only saves energy but also extends the lifespan of these components.
Supporting Energy Recovery Systems
- Integration with Energy Recovery: In advanced HVAC systems, dampers can work in conjunction with energy recovery ventilators (ERVs) or heat recovery ventilators (HRVs), optimizing the energy recovery process and enhancing overall system efficiency.
Automated Energy Saving
- Smart System Integration: Motorized or automated dampers, when integrated with smart HVAC systems, can respond dynamically to changes in environmental conditions or occupancy, adjusting airflow automatically to optimize energy usage.

10. What is the typical lifespan of an HVAC damper?
While the typical lifespan of an HVAC damper can range from 10 to 20 years, it’s influenced by the damper’s material and construction quality, type, usage frequency, environmental conditions, and maintenance regimen. Regular maintenance and timely addressing of any wear or malfunction are crucial for maximizing the lifespan of an HVAC damper.
Average Lifespan
- General Range: Under normal operating conditions, an HVAC damper can typically last between 10 to 20 years. This range is influenced by various factors, including the damper’s design and material quality.
Factors Affecting Lifespan
1. Material and Construction
- Durability of Materials: Dampers made from high-quality, durable materials like galvanized steel or aluminum tend to have a longer lifespan.
2. Type of Damper
- Manual vs. Motorized: Manual dampers, which have fewer moving parts and simpler mechanisms, often last longer than motorized dampers, which are subject to motor wear and more complex operational stresses.
3. Usage Frequency
- System Demand: Dampers in systems that are used extensively or in more demanding environments may experience more wear and tear, potentially reducing their lifespan.
4. Environmental Conditions
- Exposure to Elements: Dampers installed in areas with high humidity, fluctuating temperatures, or corrosive atmospheres may have a reduced lifespan due to increased risk of corrosion and material degradation.
Maintenance Impact
- Regular Checks and Servicing: Regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication (where applicable), and operational checks, can extend the life of an HVAC damper. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature failure.
Replacement Indicators
- Signs of Wear or Malfunction: Indications that a damper may need to be replaced include difficulty in operation (for manual dampers), unusual noises, motor failure (in motorized dampers), or visible deterioration.
11. Are there smart HVAC dampers that can be controlled remotely?
Yes, there are smart HVAC dampers available that can be controlled remotely. Smart HVAC dampers with remote control capabilities offer advanced features like wireless operation, integration with smart home systems, automated and programmable airflow management, enhanced energy efficiency, user-friendly interfaces, and additional functionalities like voice control and alerts.
Functionality of Smart HVAC Dampers
1. Remote Control
- Wireless Operation: Smart HVAC dampers can be operated wirelessly, often through a smartphone app or a home automation system, allowing users to adjust airflow remotely.
2. Integration with Smart Home Systems
- Smart Home Compatibility: These dampers can be integrated into broader smart home systems, enabling them to work in conjunction with other smart devices like thermostats, sensors, and home assistants.
Automated Airflow Management
1. Programmable Settings
- Custom Schedules: Users can create custom schedules for these dampers, automating airflow adjustments based on time of day, occupancy, or specific room requirements.
2. Responsive Adjustments
- Environmental Adaptation: Smart dampers can automatically adjust based on real-time environmental data such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, optimizing the indoor climate.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency
1. Targeted Heating and Cooling
- Zoned Temperature Control: By controlling the airflow to specific zones or rooms, smart dampers can reduce energy waste, contributing to more efficient heating and cooling.
2. Energy Usage Monitoring
- Tracking and Optimization: Some smart dampers offer features to monitor and report on energy usage, helping users identify opportunities for further efficiency improvements.
Ease of Installation and Use
User-Friendly Interface – Simple Setup and Operation: Despite their advanced capabilities, smart dampers are designed for ease of installation and user-friendly operation, making them accessible to a wide range of users.
Advanced Features
Voice Control and Alerts – Voice Command Compatibility: Many smart dampers are compatible with voice-controlled devices, and they can send alerts or notifications regarding system status or maintenance needs.

12. How do I troubleshoot common problems with HVAC dampers?
When troubleshooting common problems with HVAC dampers, it’s important to assess the type of damper (manual or motorized), check for obstructions, ensure proper power supply and control system functionality, and inspect for physical damage. Regular maintenance and early detection of issues can prevent more significant problems, ensuring the efficient operation of your HVAC system.
Damper Not Adjusting Properly
1. Manual Dampers
- Check for Obstructions: Ensure that there are no obstructions preventing the damper from moving. Sometimes, debris or dust accumulation can hinder damper movement.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: If the damper is stiff or difficult to adjust, try lubricating the moving parts to see if it improves functionality.
2. Motorized Dampers
- Inspect Motor Operation: For motorized dampers, listen for the motor operation. If the motor is silent, it might be a power issue.
- Check Power Supply: Ensure the damper is receiving power. This may involve checking batteries, wiring connections, or circuit breakers.
Uneven Airflow or Temperature Variations
- Damper Position: Check if the dampers are set in the correct position to allow the desired amount of airflow.
- System Balance: Sometimes, the issue may be with the balance of the HVAC system. Balancing the system can resolve airflow problems.
Noisy Damper Operation
- Tighten Loose Parts: Noise during operation can be due to loose components. Tighten any loose screws or fittings.
- Alignment and Wear: Check for misalignment of the damper components or signs of wear. Misaligned or worn parts may need adjustment or replacement.
Damper Not Responding to Controls
1. Manual Dampers
- Mechanical Issues: For manual dampers, ensure that the linkage between the control and the damper is intact and functioning properly.
2. Motorized Dampers
- Control System Issues: For motorized dampers, the issue might be with the control system. Check the thermostat settings and connections to the damper control system.
- Sensor Malfunction: Sometimes, the problem might be due to a malfunctioning sensor that feeds information to the damper.
Signs of Physical Damage
- Inspect for Damage: Look for signs of rust, corrosion, or physical damage on the damper. Damaged dampers might need to be repaired or replaced.
13. What is the cost range for different types of HVAC dampers?
The cost range for different types of HVAC dampers varies based on the damper type, with manual dampers being the most affordable and motorized, and zone, or safety-specific dampers like fire and smoke dampers being more expensive. Factors influencing the cost include the damper’s size, material, complexity, and any additional features for automation or safety.
Manual Dampers
- Price Range: Manual dampers are typically the most cost-effective option. The cost can range from $15 to $100 depending on the size and material.
- Factors Influencing Cost: Simplicity in design and lack of motorized components keep the cost lower. Larger and higher-quality manual dampers will be at the higher end of this price range.
Motorized/Automatic Dampers
- Price Range: Motorized dampers are more expensive due to their automated components. Prices generally range from $100 to $300 or more.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The cost is higher due to the inclusion of motors and control systems. Additional features like smart technology integration can also increase the price.
Volume Control Dampers
- Price Range: Volume control dampers can vary widely in price, typically ranging from $50 to $200.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The cost depends on the size, material, and any specialized features for precise airflow control.
Zone Dampers
- Price Range: Zone dampers, used in zoned HVAC systems, can cost anywhere from $60 to $250.
- Factors Influencing Cost: Prices vary based on the complexity of the damper, size, and integration capabilities with zoning technology.
Fire and Smoke Dampers
- Price Range: Fire and smoke dampers, which are safety-critical, can range from $150 to over $500.
- Factors Influencing Cost: These dampers are more expensive due to the stringent safety standards and materials they must adhere to. The cost can increase with the size and the specific fire or smoke rating.
Backdraft Dampers
- Price Range: Backdraft dampers are relatively affordable, generally ranging from $20 to $100.
- Factors Influencing Cost: The cost depends on the size and design, which is typically simpler than other types of dampers.

14. Can dampers be used in both residential and commercial HVAC systems?
Yes, dampers can be used in both residential and commercial HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. They play a critical role in airflow control, system balancing, temperature regulation, indoor air quality, and energy efficiency. While their application may vary in complexity between residential and commercial systems, their fundamental function remains the same. Adaptability and compliance with safety standards are key aspects of their use in both types of environments.
Application in Residential HVAC Systems
- Airflow Control: In residential systems, dampers are used to control and direct airflow to different zones or rooms within a home. This helps in maintaining comfortable temperatures throughout and can lead to energy savings by heating or cooling only occupied areas.
- System Balancing: Dampers in residential HVAC systems can be crucial for balancing the system, ensuring that each room receives an appropriate amount of conditioned air.
Use in Commercial HVAC Systems
- Complex Air Management: Commercial HVAC systems, which often serve larger and more complex buildings, use dampers for more sophisticated air management. These systems may require precise control over airflow to different zones or floors.
- Advanced Dampers for Large Systems: Commercial systems might use motorized or automated dampers that can be integrated into building management systems for optimal efficiency and control.
Similarities in Function
- Regulating Temperature and Air Quality: In both types of systems, dampers help regulate temperature and improve indoor air quality by controlling the distribution of conditioned air and preventing the mixing of fresh and return air.
- Energy Efficiency: Proper use of dampers in both residential and commercial systems can enhance energy efficiency, reducing unnecessary heating and cooling.
Adaptability to System Requirements
- Customizable Solutions: Dampers come in various sizes and designs, making them adaptable to the specific needs of both residential and commercial HVAC systems. Customizable solutions are available to fit the unique requirements of different buildings.
Safety and Compliance
- Fire and Smoke Dampers: In both settings, safety is a priority. Fire and smoke dampers are used to prevent the spread of fire and smoke through the ductwork, complying with safety regulations in residential and commercial buildings.
15. How do I properly size an HVAC damper for my ductwork?
Properly sizing an HVAC damper involves measuring ductwork dimensions accurately, selecting a damper that corresponds to these dimensions, considering the duct shape, accounting for system airflow needs, determining the type of damper, factoring in installation space, consulting manufacturer’s guidelines, and seeking professional advice if needed. Correct sizing is essential for the efficient and effective operation of your HVAC system, ensuring optimal airflow control and energy efficiency.
1. Measure Ductwork Dimensions
- Accurate Measurements: Begin by accurately measuring the dimensions of your ductwork. This includes the width, height, and diameter (for round ducts) of the duct where the damper will be installed.
2. Select the Corresponding Damper Size
- Match Damper to Duct Size: Choose a damper that matches or is very close to the size of your ductwork. Dampers are typically sized to fit standard duct sizes, so ensure the damper’s dimensions align with your measurements.
3. Consider the Duct Shape
- Shape Compatibility: Ensure the damper is designed for the shape of your ducts (round, rectangular, square). Using the wrong shape can result in poor fit and air leaks.
4. Account for System Requirements
- Airflow Needs: Consider the airflow requirements of your HVAC system. The damper should be capable of handling the system’s maximum airflow without causing excessive pressure drops or noise.
5. Determine Damper Type
- Manual or Motorized: Decide whether a manual or motorized damper is more suitable for your needs. This choice may affect the sizing, as motorized dampers might have different specifications due to their additional components.
6. Factor in the Installation of Space
- Space Constraints: Consider the space available around the ductwork for damper installation. Ensure there is enough room to accommodate the damper and any necessary mechanisms or controls.
7. Consult HVAC Guidelines
- Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Refer to the damper manufacturer’s sizing guidelines. Manufacturers often provide specifications and sizing charts that can assist in selecting the appropriate size.
8. Professional Assessment
- Expert Advice: If you are unsure about the correct size, consult with an HVAC professional. An expert can provide valuable advice and ensure that the damper fits perfectly with your ductwork and meets the system’s requirements.

16. What are the signs that an HVAC damper needs to be replaced?
Signs that an HVAC damper needs to be replaced include inconsistent or poor airflow, unusual noises, visible physical damage, difficulty operating manual dampers, issues with motorized dampers, higher energy bills, age-related wear, and compatibility issues with system upgrades. Identifying and addressing these signs promptly can help maintain the efficiency and reliability of your HVAC system.
Inconsistent or Poor Airflow
- Uneven Temperature Distribution: If certain areas are not receiving adequate airflow, resulting in uneven heating or cooling, this could indicate that a damper is not functioning properly.
- Lack of Air Control: Difficulty in managing airflow to specific zones or rooms may be a sign of damper failure.
Noises from the Ductwork
- Rattling or Banging Sounds: Unusual noises emanating from the ducts, especially near the damper’s location, can signal a problem. This may be due to loose or broken damper components.
Physical Damage
- Visible Wear or Corrosion: Inspect the damper for signs of physical damage, rust, or corrosion, particularly in metal dampers. Such damage can impair the damper’s functionality.
Difficulty in Operating Manual Dampers
- Stiffness or Jamming: If a manual damper is difficult to adjust, or if it’s stuck in one position, it may need to be replaced.
Motorized Damper Failures
- Non-Responsive Motorized Dampers: For motorized dampers, a lack of response when adjustments are made through the control system can indicate a problem. This could be due to motor failure or issues with the control mechanism.
Increased Energy Bills
- Higher Than Normal Costs: An unexpected increase in energy bills can sometimes be traced back to malfunctioning dampers. Inefficient dampers can cause the HVAC system to work harder, consuming more energy.
Age and Wear
- Beyond Expected Lifespan: Consider the age of the damper. Dampers that have been in service beyond their expected lifespan may start to fail and could require replacement.
System Upgrades
- Compatibility with New HVAC Systems: If you’re upgrading your HVAC system, existing dampers may not be compatible with the new setup. In such cases, replacing dampers can be necessary to ensure optimal system performance.
17. How do HVAC dampers impact airflow and temperature control?
HVAC dampers impact airflow and temperature control by regulating the direction and volume of air, enabling zoned heating and cooling, balancing the HVAC system, enhancing efficiency, preventing overheating and overcooling, improving indoor air quality, and adapting to environmental changes. Their operation significantly impacts how air is distributed throughout a building, affecting both comfort and efficiency.
Regulation of Airflow
- Direction and Volume of Air: Dampers control the direction and volume of air moving through the ductwork. By adjusting their position, they can either increase or decrease the amount of air flowing to different parts of the building.
Temperature Control
- Zoned Heating and Cooling: In systems with zoning capabilities, dampers can be used to create different temperature zones within a building. This allows for customized temperature control in various areas, catering to different comfort preferences or occupancy patterns.
Balancing the HVAC System
- Even Distribution of Air: Properly adjusted dampers ensure that air is evenly distributed throughout the building. This helps in preventing areas that are too hot or too cold, leading to a more balanced and comfortable environment.
Enhancing System Efficiency
- Reducing Energy Waste: By directing air where it’s needed and limiting it where it’s not, dampers can reduce energy waste. This targeted approach to airflow helps in maintaining desired temperatures more efficiently.
Preventing Overheating and Overcooling
- Optimal Use of HVAC Equipment: Dampers prevent certain parts of the HVAC system from overworking. By managing airflow, they help maintain the desired temperature without overtaxing the system, thereby extending the life of HVAC equipment.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
- Air Circulation: Good air circulation, facilitated by dampers, is essential for maintaining indoor air quality. Properly functioning dampers ensure that fresh air is adequately circulated, while stale air is removed.
Adapting to Environmental Changes
- Responsive Adjustments: In advanced HVAC systems, dampers can adjust automatically to changes in the internal or external environment, such as temperature fluctuations or varying occupancy levels.

18. Are there regulations or codes that pertain to HVAC damper installation?
Yes, there are specific regulations and codes that pertain to HVAC damper installation. These include local and national building codes, fire and safety regulations, energy efficiency standards, air quality standards, mechanical codes, and manufacturer’s guidelines. These regulations are designed to ensure the safety, efficiency, and proper functionality of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.
Building Codes
- Local and National Standards: HVAC damper installations must comply with local and national building codes. These codes dictate the proper installation methods, materials, and safety standards to be followed.
Fire and Safety Regulations
- Fire Dampers: Special regulations pertain to fire dampers, which are crucial for preventing the spread of fire and smoke through ductwork. These dampers must comply with fire safety standards and are typically required to be installed in specific locations, such as where ductwork passes through fire-rated barriers.
- Smoke Dampers: Similarly, smoke dampers must comply with regulations that ensure they properly prevent the spread of smoke within HVAC systems in the event of a fire.
Energy Efficiency Standards
- Reducing Energy Consumption: Certain codes may specify requirements for dampers in terms of energy efficiency, ensuring that they contribute to the overall energy efficiency of the HVAC system.
Air Quality Standards
- Indoor Air Quality: Some regulations focus on indoor air quality (IAQ) and may dictate requirements for dampers used in ventilation and air filtration systems.
Mechanical Codes
- HVAC System Requirements: Mechanical codes provide guidelines on the installation of all HVAC components, including dampers, to ensure they are correctly integrated into the overall system.
Manufacturer’s Installation Guidelines
- Compliance with Specifications: Following the manufacturer’s installation guidelines is also essential. These guidelines are designed to ensure that dampers function as intended and meet the performance standards set by the manufacturer.
Inspection and Compliance
- Professional Verification: Post-installation, it’s often necessary to have the work inspected by a professional to ensure it complies with all relevant codes and regulations.
19. What are the innovative trends or advancements in HVAC damper technology?
Innovative trends and advancements in HVAC damper technology, such as smart controls, IoT integration, focus on energy efficiency, improved air quality sensors, zoned temperature control, aerodynamic designs, self-diagnosing features, and compatibility with building management systems, are transforming the way HVAC systems operate. These advancements contribute to more efficient, user-friendly, and environmentally sustainable heating, ventilation, and air conditioning solutions.
Smart Damper Controls
- Automated Adjustments: One of the significant advancements is the integration of smart controls in HVAC dampers. These systems can automatically adjust damper positions based on real-time data, such as temperature changes, air quality, and occupancy patterns.
Integration with IoT Devices
- Internet of Things (IoT): Modern dampers are increasingly being integrated with IoT devices. This allows for remote monitoring and control via smartphones or other smart devices, providing greater convenience and enhanced system management.
Energy Efficiency Focus
- Green Technology: Advancements in damper technology are increasingly focusing on energy efficiency. Newer designs aim to reduce energy consumption and improve the overall carbon footprint of HVAC systems.
Improved Air Quality Sensors
- Air Quality Optimization: Dampers equipped with advanced air quality sensors can regulate airflow more effectively to maintain optimal indoor air quality. These sensors can detect pollutants, humidity levels, and other environmental factors.
Zoned Temperature Control
- Precision in Climate Management: Advanced damper systems allow for precise zoned temperature control, catering to the specific heating and cooling needs of different areas within a building.
Aerodynamic Designs
- Reduced Noise and Pressure Drop: Modern dampers are being designed with aerodynamics in mind to reduce noise levels and minimize pressure drop across the damper, enhancing the overall efficiency of the HVAC system.
Self-Diagnosing Features
- Maintenance and Alerts: Some advanced dampers come with self-diagnosing capabilities, alerting users to maintenance needs or system issues, which aids in preventative maintenance and reduces downtime.
Compatibility with Building Management Systems
- Seamless Integration: New damper technologies are designed for seamless integration with existing building management systems (BMS), allowing for centralized control and monitoring of the entire HVAC system.

Need High-quality HVAC Grilles and Diffusers? Shoot us a message, and I’ll be happy to assist you in picking the right grilles or diffusers for your needs.