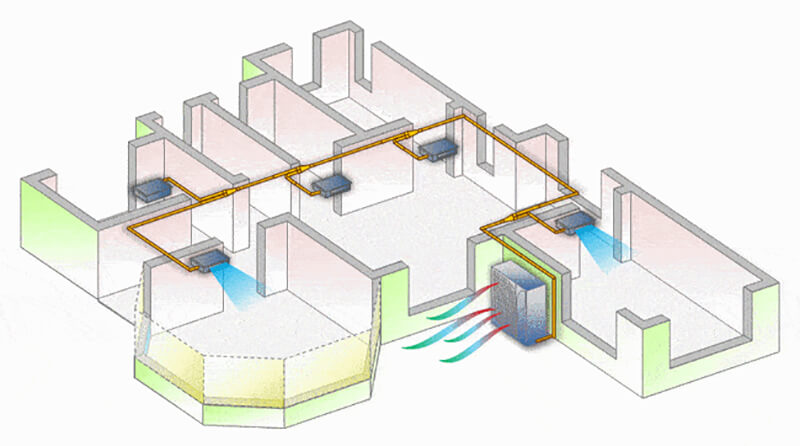
In the modern world, where we spend a significant portion of our time indoors, the quality of the air we breathe is paramount. Fresh-air ventilation plays a crucial role in ensuring a healthy and comfortable indoor environment. It involves bringing fresh outdoor air into a building and is essential for diluting indoor pollutants and replenishing oxygen levels.
While traditional HVAC systems focus on heating, cooling, and circulating indoor air, integrating fresh-air ventilation adds a new dimension to these systems. This integration allows for a continuous supply of fresh air, significantly improving indoor air quality.
This article aims to explore the importance of fresh-air ventilation, how it can be effectively integrated into existing HVAC systems and the benefits it brings to indoor environments.

Understanding Fresh-Air Ventilation
At its core, fresh-air ventilation refers to the process of introducing outdoor air into a building’s interior environment. Unlike traditional HVAC systems that mainly recirculate indoor air, fresh-air ventilation systems ensure a continuous influx of outside air, crucial for maintaining healthy indoor air quality.
- Importance of Fresh Air: Fresh air reduces the concentration of indoor pollutants like carbon dioxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and other airborne contaminants. This is essential for preventing what is commonly known as ‘sick building syndrome’.
Differentiating Fresh-Air Ventilation from Air Circulation
While both are integral to HVAC systems, fresh-air ventilation and air circulation serve distinct roles. Air circulation involves the movement of air within indoor spaces for heating or cooling purposes, whereas fresh-air ventilation is about replacing stale indoor air with fresh outdoor air.
- Recirculated Air vs. Fresh Air: Recirculated air can accumulate pollutants over time. Fresh-air ventilation counters this by introducing new, cleaner air into the building.
Benefits of Fresh-Air Ventilation
Integrating fresh-air ventilation into HVAC systems offers several key benefits:
- Improved Air Quality: By diluting pollutants, fresh-air systems help maintain a healthier indoor air quality.
- Enhanced Comfort: Fresh air can reduce odors and humidity levels, contributing to a more comfortable living or working environment.
- Health Benefits: Good ventilation has been linked to reduced symptoms of asthma, allergies, and other respiratory problems.
Understanding Ventilation Needs
Determining the right amount of fresh-air ventilation depends on various factors, including building occupancy, size, and local environmental conditions. It’s not a one-size-fits-all solution; the ventilation needs of a crowded office will differ significantly from those of a residential home.
- Assessing Ventilation Requirements: Professional assessment can help determine the optimal level of ventilation needed to maintain indoor air quality without compromising energy efficiency.
The Role of HVAC in Ventilation
Understanding the fundamental workings of HVAC systems is key to comprehending their role in ventilation. Traditionally, HVAC systems are designed to control the temperature and circulate air within indoor spaces, primarily through heating and cooling processes.
- Traditional HVAC Operations: These systems recirculate the same indoor air, adjusting its temperature to maintain comfort levels.
Incorporating Ventilation into HVAC
While temperature control is a primary function, modern HVAC systems can be enhanced to include fresh-air ventilation. This integration significantly improves indoor air quality by introducing and circulating fresh air from the outside.
- Benefits of Ventilation in HVAC: Adding ventilation capabilities to HVAC systems helps dilute indoor air pollutants and brings in necessary oxygen, enhancing the overall air quality.
Challenges in Integrating Fresh-Air Ventilation
Integrating fresh-air ventilation into existing HVAC systems can present certain challenges:
- System Compatibility: Not all existing HVAC systems may be readily compatible with ventilation upgrades.
- Balancing Energy Efficiency: Additional energy is required to heat or cool the incoming fresh air, which can impact the overall energy efficiency of the system.
Solutions and Innovations
Despite the challenges, there are several ways to successfully integrate fresh-air ventilation into HVAC systems:
- Retrofitting Existing Systems: Many HVAC systems can be retrofitted with components like air dampers or energy recovery ventilators to add ventilation capabilities.
- Advanced HVAC Designs: Newer HVAC systems are increasingly being designed with built-in fresh-air ventilation features, balancing air quality with energy efficiency.
Future Trends in HVAC and Ventilation
The future of HVAC technology points towards systems that are more integrated and efficient. Innovations in smart technology and sustainable design are expected to further enhance the ability of HVAC systems to provide both optimal climate control and high-quality indoor air.

Types of Fresh-Air Ventilation Systems
In the quest to improve indoor air quality, several types of fresh-air ventilation systems have been developed. Each system offers unique features and benefits, making them suitable for varying building needs and climatic conditions.
Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs)
Heat Recovery Ventilators are designed to efficiently manage energy while introducing fresh air. They achieve this by capturing heat from the outgoing stale air and using it to warm the incoming fresh air.
- Energy Efficiency in Cold Climates: HRVs are particularly effective in cold climates, reducing the need for additional heating.
- Application Suitability: Ideal for environments with larger temperature differences between inside and outside.
Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs)
Energy Recovery Ventilators function similarly to HRVs but with an added ability to manage humidity levels. They transfer moisture along with heat, maintaining a comfortable indoor atmosphere.
- Managing Indoor Humidity: ERVs are beneficial in regions where controlling indoor humidity is crucial, whether in humid or arid climates.
- Versatile Climate Adaptability: Suitable for a wide range of climatic conditions, both warm and cold.
Balanced Ventilation Systems
Balanced Ventilation Systems provide an equal exchange of indoor and outdoor air without energy recovery. Separate fans are used for exhaust and intake, ensuring balanced air flow.
- Controlled Air Exchange: These systems offer precise control over air exchange rates, which can be optimized for air quality.
- Widespread Application: A practical choice for buildings where energy recovery is less of a priority.
Smart Ventilation Solutions
The advent of smart ventilation technologies has brought a new level of efficiency and adaptability. These systems use sensors and automation to adjust ventilation based on real-time indoor and outdoor conditions.
- Dynamic Air Quality Management: Smart systems adapt ventilation rates to occupancy levels, indoor pollutant concentrations, and even external air quality.
- Optimized for Comfort and Efficiency: They strike a balance between maintaining air quality and energy conservation, responding intelligently to occupant needs.
Design and Installation Considerations
The design of a fresh-air ventilation system is critical for its effectiveness and efficiency. Several key principles must be considered to ensure optimal performance and integration with existing HVAC systems.
- Assessing Building Requirements: Understanding the specific needs of the building, such as its size, layout, occupancy, and local climate, is essential in designing an effective system.
- Airflow Management: Designing for appropriate airflow patterns and rates is crucial to avoid issues like air stagnation or drafts.
Integration Challenges with Existing HVAC Systems
Integrating a fresh-air system into an existing HVAC setup can present unique challenges:
- Compatibility with Current Systems: Ensuring that the new ventilation system works harmoniously with the existing HVAC components is vital for overall system efficiency.
- Space and Infrastructure Constraints: Consideration must be given to the physical space available for installing additional components like ductwork or ventilators.
Professional Assessment and Planning
A professional assessment is often necessary to navigate these challenges effectively.
- Expertise in System Design: HVAC professionals can provide valuable insights and recommendations based on the building’s specific requirements and constraints.
- Customized Solution Development: A tailored approach is typically needed to develop a solution that optimizes both air quality and energy efficiency.
Installation Process and Best Practices
The installation of a fresh-air ventilation system requires careful planning and execution.
- Adhering to Standards and Codes: Installation must comply with relevant building codes and industry standards to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Collaboration with Qualified Contractors: Working with experienced contractors who specialize in HVAC systems is crucial for a successful installation.
Technological Integration and Smart Controls
Incorporating advanced technology and smart controls can enhance the functionality of fresh-air systems.
- Automated Systems: Utilizing automation for controlling airflow and monitoring air quality can significantly improve the efficiency and responsiveness of the system.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Implementing user-friendly controls allows for easy management and adjustments of the ventilation system as needed.
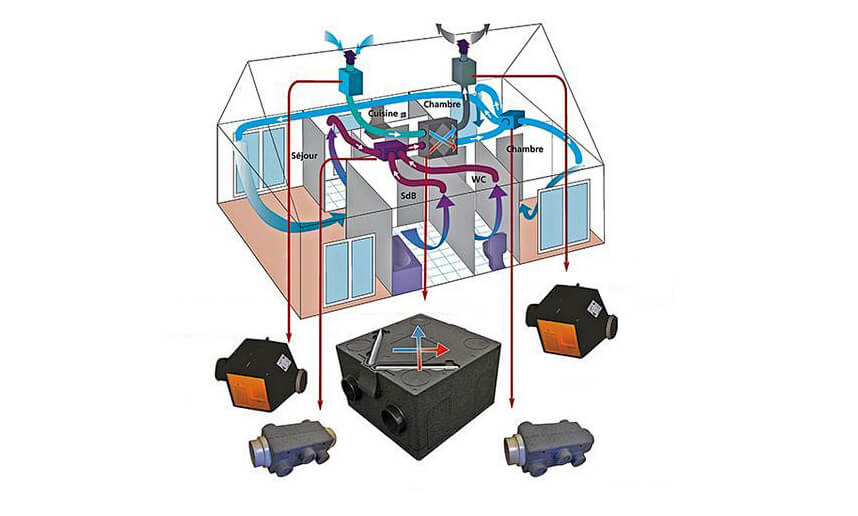
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Incorporating fresh-air ventilation into HVAC systems raises important considerations about energy efficiency. The goal is to achieve optimal indoor air quality without significantly increasing energy consumption.
- Energy Impacts of Ventilation: Fresh-air systems can increase the load on HVAC systems, as they require heating or cooling of incoming air, especially in extreme weather conditions.
- Strategies for Energy-Efficient Ventilation: Employing energy recovery technologies and smart control systems can help mitigate these energy impacts, maintaining a balance between air quality and energy usage.
Utilizing Energy Recovery Solutions
Energy recovery technologies, such as Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs) and Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs), play a crucial role in reducing the energy demands of fresh-air ventilation.
- Heat and Moisture Transfer: These systems recover heat (and in the case of ERVs, also moisture) from the outgoing air to precondition the incoming fresh air, thereby reducing the energy required for heating or cooling.
- Optimal Use in Various Climates: The effectiveness of HRVs and ERVs varies depending on the climate, making the selection of the right system for a specific location essential.
Sustainable Practices in Ventilation
Adopting sustainable practices in ventilation system design and operation can further enhance energy efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Smart and Automated Systems: Leveraging smart ventilation systems that adjust airflow based on real-time data can optimize energy use.
- Use of Renewable Energy Sources: Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar power, to operate ventilation systems can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of buildings.
The Future of Sustainable Ventilation
Looking ahead, the future of fresh-air ventilation is closely tied to innovations in sustainable technologies and practices.
- Advancements in Energy Recovery: Ongoing research and development in energy recovery and HVAC efficiency promise more effective and sustainable ventilation solutions.
- Integration with Green Building Practices: Fresh-air ventilation systems are becoming a key component of green building certifications and standards, reflecting their importance in sustainable building design.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Incorporating fresh-air ventilation into HVAC systems is not just about technical integration but also about complying with regulatory standards and codes. These regulations are designed to ensure safety, efficiency, and environmental protection.
- Importance of Compliance: Adhering to regulatory standards is crucial for legal compliance, system performance, and occupant safety.
Key Standards and Codes in HVAC
Understanding and following the relevant building codes and HVAC standards is essential for any fresh-air ventilation project.
- ASHRAE Guidelines: The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) provides comprehensive guidelines on ventilation and indoor air quality.
- Local and National Building Codes: These codes vary by region and can have specific requirements for ventilation systems, including minimum fresh air rates and system design.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Regulations
Energy efficiency and environmental impact are increasingly important factors in HVAC design, influenced by various energy and environmental regulations.
- Energy Star and LEED Certification: Programs like Energy Star for HVAC systems and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) for buildings set benchmarks for energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
- Reducing Carbon Footprint: Regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption can affect the choice and design of ventilation systems.
Compliance in System Design and Installation
Ensuring compliance during both the design and installation phases is critical to the success of integrating fresh-air ventilation.
- Professional Assessments for Compliance: Working with HVAC professionals who are knowledgeable about current regulations ensures that the system design and installation are compliant.
- Regular Updates on Regulatory Changes: Keeping abreast of changes in regulations and standards is important for ongoing compliance and system upgrades.

Cost Considerations and ROI
When considering the addition of fresh-air ventilation to an HVAC system, it’s important to understand the financial implications and potential return on investment (ROI). This evaluation helps in making informed decisions about the feasibility and long-term benefits of the upgrade.
Initial Investment and Installation Costs
The initial cost of integrating a fresh-air ventilation system includes several components:
- Equipment Expenses: The cost of the ventilation unit itself, varies based on the type and capacity of the system.
- Installation Charges: Professional installation costs, can differ depending on the complexity of the integration and the specific requirements of the building.
- Additional Infrastructure: Potential costs for additional ductwork, controls, and other necessary infrastructure changes.
Analyzing Long-Term ROI
While the upfront costs might be substantial, the long-term ROI of fresh-air ventilation systems can be quite significant.
- Energy Savings: Improved air quality can lead to better health and productivity, potentially reducing healthcare and operational costs.
- Enhanced Building Value: Buildings with advanced HVAC systems, including efficient ventilation, may have a higher market value and appeal.
Understanding Operational Expenses
The operational costs of running a fresh-air ventilation system include energy consumption and maintenance expenses.
- Energy Efficiency Factors: Systems with energy recovery capabilities, like ERVs and HRVs, can offset some of the additional energy costs by reducing the need for heating or cooling the incoming air.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular maintenance is crucial for system efficiency and longevity, and this incurs ongoing costs.
Financial Incentives and Rebates
Investigating potential financial incentives can help offset the initial costs.
- Government and Utility Rebates: Some regions offer rebates or incentives for installing energy-efficient systems.
- Tax Benefits: There may be tax benefits or deductions available for energy-efficient upgrades.
Conclusion
As we have explored, integrating fresh-air ventilation into HVAC systems is more than just an upgrade; it’s a significant step towards healthier, more comfortable indoor environments. The inclusion of fresh air not only enhances air quality but also contributes to the overall well-being of occupants.
Summarizing Key Takeaways
This article has outlined the various aspects of fresh-air ventilation systems, from understanding their basic principles, types, and designs, to considering the energy efficiency, costs, and regulatory compliance involved in their implementation.
Encouraging a Shift Towards Healthier Living Spaces
The move towards integrating fresh-air ventilation in buildings is not just a trend but a necessary shift in how we approach indoor environmental quality. It represents a commitment to promoting healthier living and working spaces.
Final Thoughts on Future Trends
Looking ahead, advancements in HVAC technology and a growing emphasis on sustainability suggest that fresh-air ventilation will become an even more integral part of building design. As awareness of indoor air quality continues to rise, so will the adoption of these systems.
- Continued Innovation in HVAC: The future holds promise for more innovative, efficient, and user-friendly ventilation solutions.
- Advocacy for Healthier Buildings: The push for healthier indoor environments will likely influence more stringent regulations and building codes, further promoting the adoption of fresh-air systems.
Invitation to Action
Whether you are a building owner, an HVAC professional, or simply someone interested in improving indoor air quality, the information presented in this article provides a foundation for considering fresh-air ventilation in your HVAC planning and decision-making.

If you want to know more, please click below:
- Grilles, Registers & Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Linear Slot Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Egg Crate Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Jet Nozzle Diffuser – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Linear Bar Grilles – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Air Swirl Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- Round Ceiling Diffusers – The Ultimate Guide
- Exhaust Air Louver – The Ultimate Guide
- HVAC Registers – The Ultimate Guide